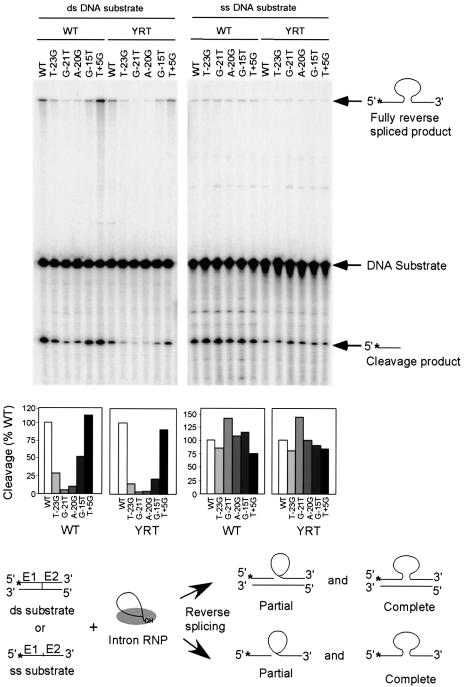
Fig. 2. Reverse splicing assay with double- and single-stranded DNA target sites. Reverse splicing was assayed by incubating wild-type or YRT mutant RNP particles with 5′-top-strand labeled double- or single-stranded 70mer DNAs containing the wild-type target sequence (positions –35 to +35) or the indicated mutations. The products were analyzed in a denaturing 6% polyacrylamide gel, which was dried and quantitated with a PhosphorImager. Labeled products are indicated to the right of the gel, with the position of the label indicated by an asterisk. The schematic at the bottom diagrams reverse splicing of the intron RNA into double- or single-stranded DNA. Partial reverse splicing results in cleaved 5′-exon (the predominant product) and intron lariat linked to 3′-exon (not labeled), while complete reverse splicing results in insertion of linear intron RNA between the two DNA exons. The bar graphs show reverse splicing activity relative to the wild-type DNA target site based on quantitation of the partially and fully reverse spliced products.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.