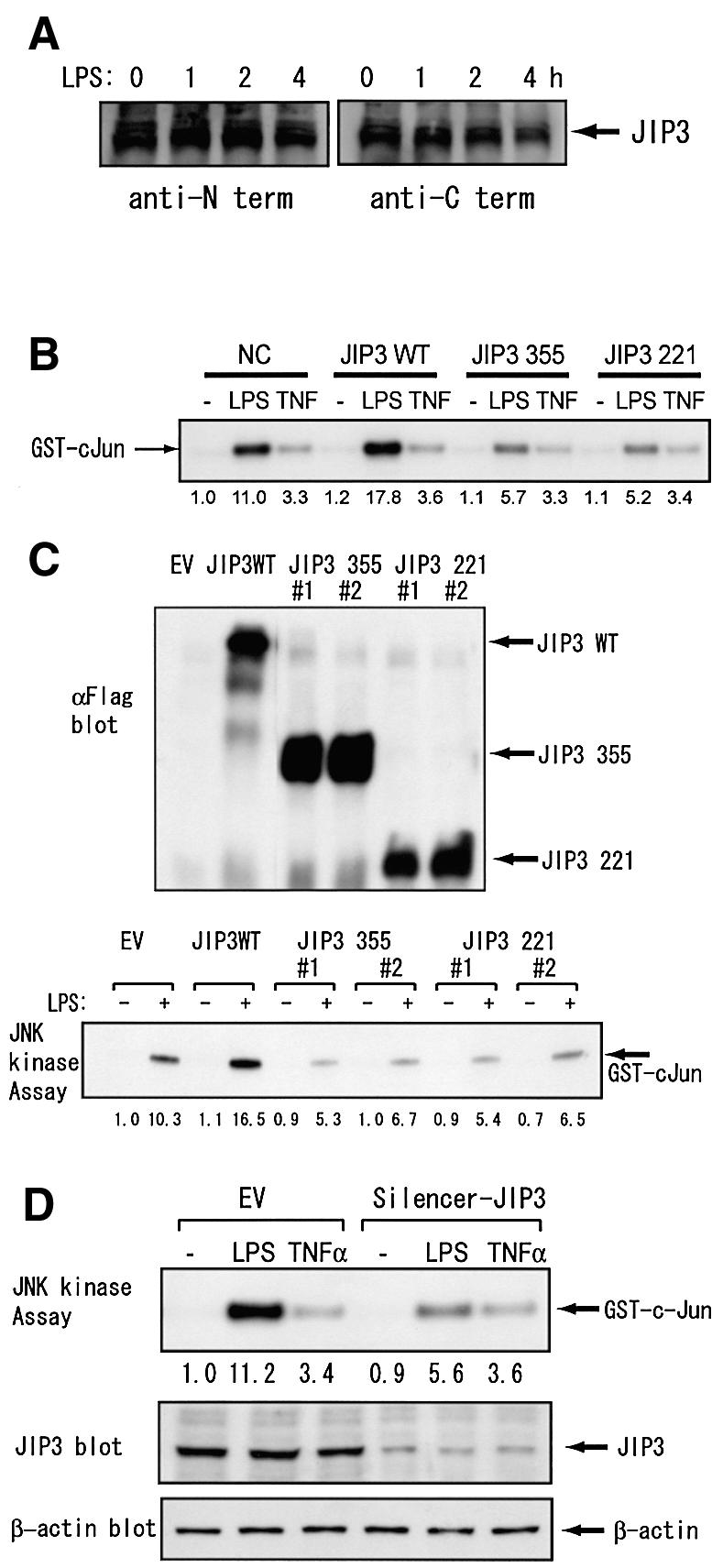
Fig. 5. JIP3 is involved in JNK activation by LPS in a mouse macrophage cell line. (A) RAW264.7 cells were stimulated with 1 µg/ml LPS for the indicated times. Cell lysates were prepared and JIP3 protein contents were analyzed by antibodies specific to the N- and C-terminal domains of JIP3. (B) RAW264.7 cells were transiently transfected with the empty vector, the expression plasmid of the wild-type JIP3 or a JIP3 C-terminal mutant, in combination with the expression plasmid for HA-tagged JNK1. Cells were untreated, treated with 1 µg/ml LPS or 10 ng/ml TNF-α for 20 min, and anti-HA antibody immunoprecipitates were examined for their kinase activity on GST–cJun5-89. (C) RAW264.7 cells stably transfected with the empty vector, the expression plasmid of the wild-type JIP3, or a JIP3 C-terminal mutant were either untreated or treated with 1 µg/ml LPS for 20 min, and anti-JNK1 immunoprecipitates were examined for their kinase activity on GST–cJun5-89. Cell lysates were also examined for the exogenous JIP3 expression with anti-Flag antibody. (D) RAW264.7 cells were stably transfected with either the empty vector or the pSilencer-JIP3 plasmid. Cells were untreated, treated with 1 µg/ml LPS or 10 ng/ml TNF-α for 20 min. JIP3 and β-actin protein contents were examined by their specific antibodies. Subsequently, JNK1 was immunoprecipitated and in vitro kinase assay was performed on GST–cJun5-89.
