Abstract
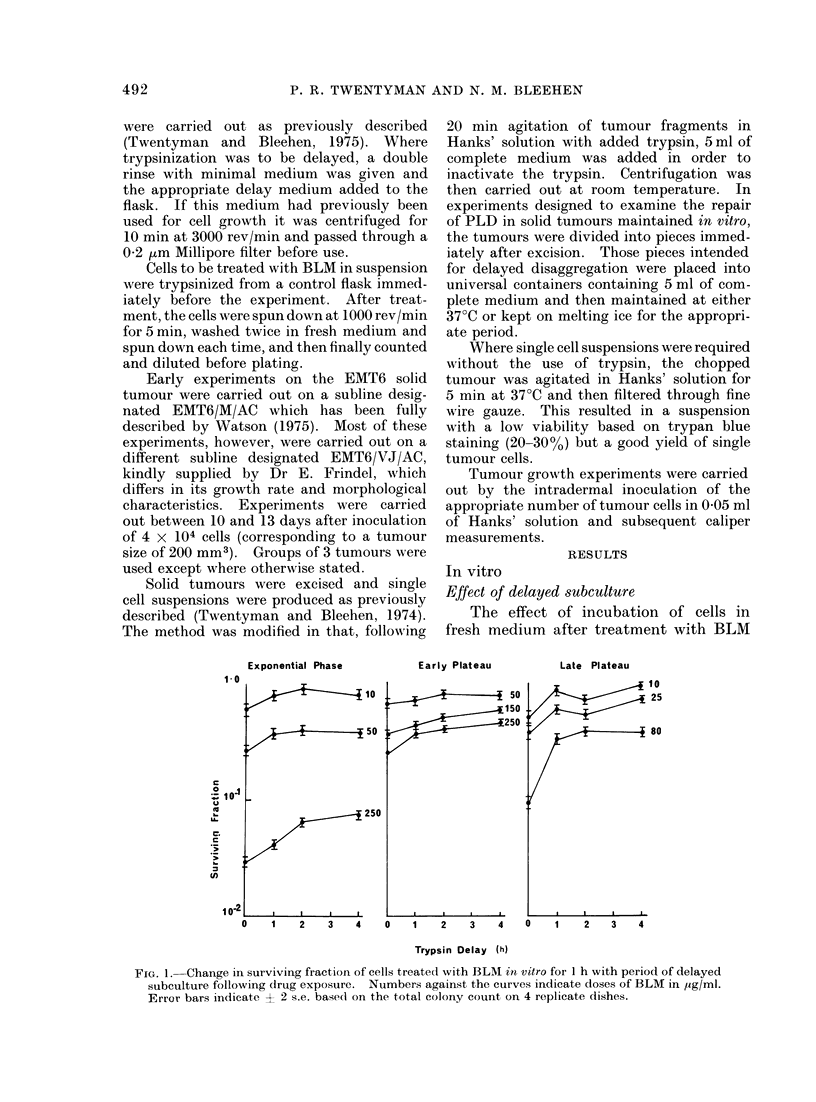
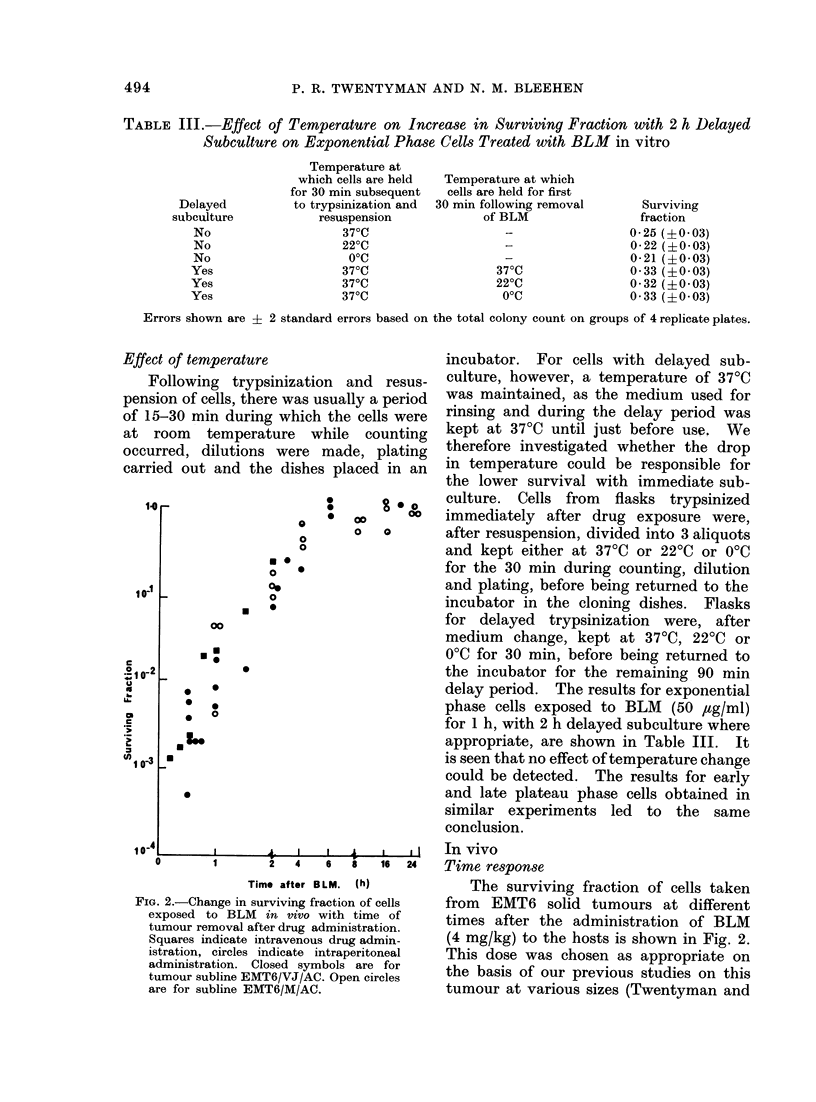
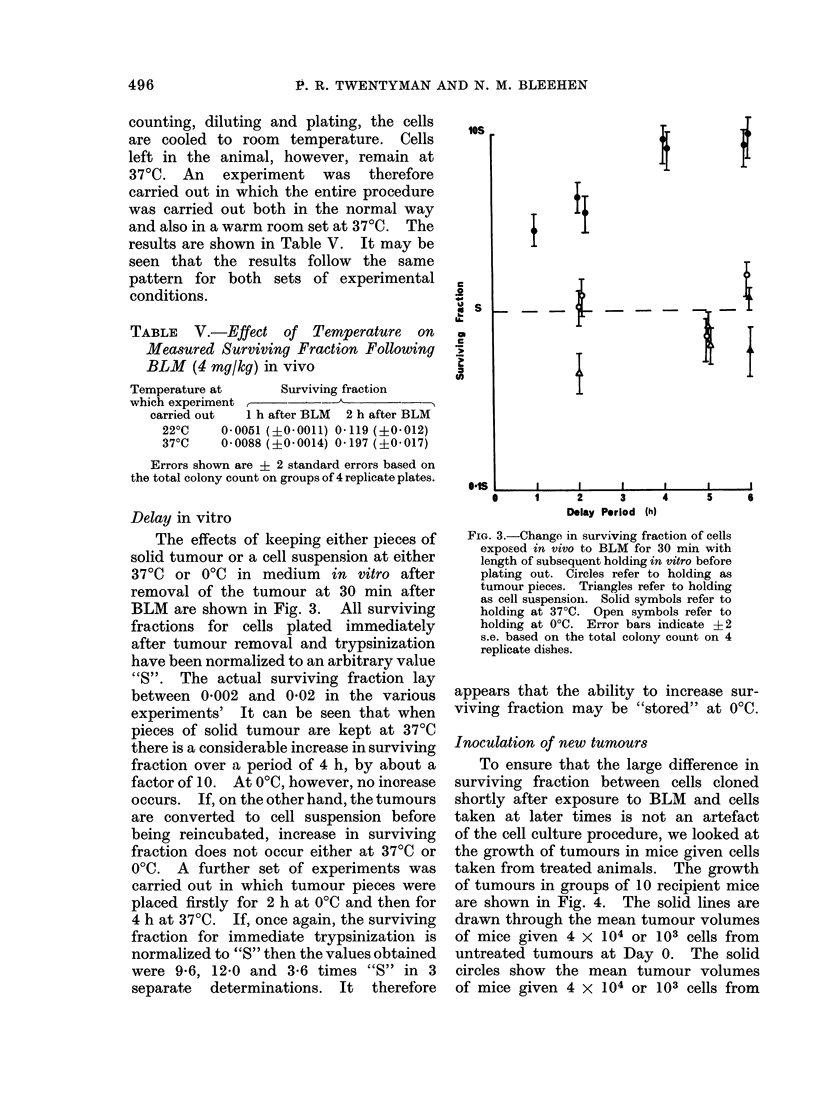
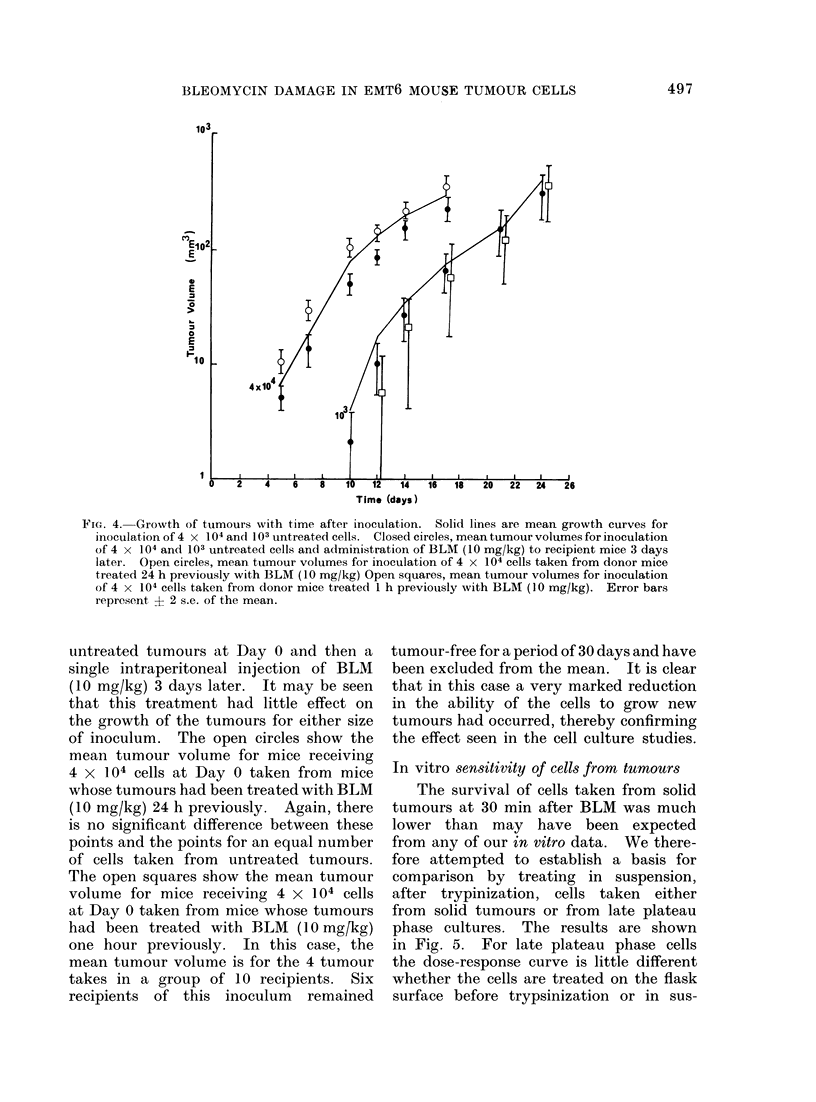
Studies have been carried out into the effect usually referred to as "repair to potentially lethal damage" following the treatment of cells with bleomycin. In vitro, increased survival was seen with delayed subculture of cells in both exponential phase and plateau phase. It was unimportant whether the medium present during the delay period had been previously used to support cell growth. Exposure of cells growing as a solid tumour in vivo to bleomycin (4 mg/kg), gave a surviving fraction of 2 X 10(-3) if assay was carried out at 30 min but a surviving fraction of virtually 100% if assay was delayed until 6 h. Various possible artefacts have been eliminated as reasons for the observations but doubts are raised regarding the nature of the mechanism involved.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barranco S. C., Novak J. K., Humphrey R. M. Studies on recovery from chemically induced damage in mammalian cells. Cancer Res. 1975 May;35(5):1194–1204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belli J. A., Shelton M. Potentially lethal radiation damage: repair by mammalian cells in culture. Science. 1969 Aug 1;165(3892):490–492. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3892.490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleehen N. M., Gillies N. E., Twentyman P. R. The effect of bleomycin and radiation in combination on bacteria and mammalian cells in culture. Br J Radiol. 1974 Jun;47(558):346–351. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-47-558-346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto J. Radioautographic studies on the intracellular distribution of bleomycin-14C in mouse tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1974 Nov;34(11):2969–2974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn G. M., Little J. B. Plateau-phase cultures of mammalian cells: an in vitro model for human cancer. Curr Top Radiat Res Q. 1972 Jul;8(1):39–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn G. M., Ray G. R., Gordon L. F., Kallman R. F. Response of solid tumor cells exposed to chemotherapeutic agents in vivo: cell survival after 2- and 24-hour exposure. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Feb;50(2):529–533. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.2.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. B., Hahn G. M., Frindel E., Tubiana M. Repair of potentially lethal radiation damage in vitro and in vivo. Radiology. 1973 Mar;106(3):689–694. doi: 10.1148/106.3.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. B. Repair of potentially-lethal radiation damage in mammalian cells: enhancement by conditioned medium from stationary cultures. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1971;20(1):87–92. doi: 10.1080/09553007114550921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima T., Kuwano M., Matsui K., Komiyama S., Hiroto I. Potentiation of bleomycin by an antifungal polyene, pentamycin, in transformed animal cells. Cancer Res. 1974 Dec;34(12):3258–3261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips R. A., Tolmach L. J. Repair of potentially lethal damage in x-irradiated HeLa cells. Radiat Res. 1966 Nov;29(3):413–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray G. R., Hahn G. M., Bagshaw M. A., Kurkjian S. Cell survival and repair of plateau-phase cultures after chemotherapy--relevance to tumor therapy and to the in vitro screening of new agents. Cancer Chemother Rep. 1973 Nov-Dec;57(4):473–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rockwell S. C., Kallman R. F., Fajardo L. F. Characteristics of a serially transplanted mouse mammary tumor and its tissue-culture-adapted derivative. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Sep;49(3):735–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takabe Y., Miyamoto T., Terashima T. Demonstration of repair of potentially lethal damage in plateau phase cells of Ehrlich ascites tumor after exposure to bleomycin. Gan. 1974 Dec;65(6):559–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twentyman P. R., Bleehen N. M. The sensitivity to bleomycin of a solid mouse tumour at different stages of growth. Br J Cancer. 1974 Nov;30(5):469–472. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1974.222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


