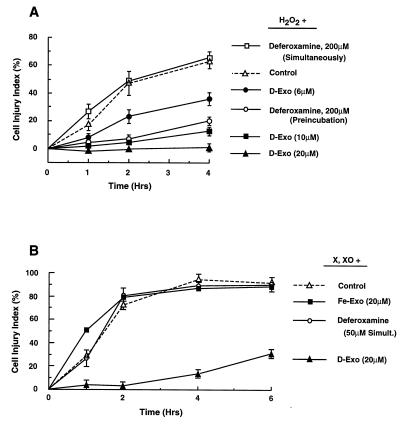
Figure 2.
Desferri-exochelins protect cultured adult rat cardiac myocytes against injury from exposure to reactive oxygen species. Cell injury to myocytes in Krebs–Ringer bicarbonate buffer containing 5% fetal bovine serum was quantitated by measuring LDH release and calculating a cell injury index, as described in the text. (A) Concentrations of desferri-exochelin 784SM ranging from 6 to 20 μM reduced cell injury in a concentration-dependent manner when given simultaneously with 100 μM H2O2 for 4 hr (P < 0.001 by repeated measures ANOVA) (n = 9 in each group). Deferoxamine (200 μM) reduced injury if added 2 hr before exposure to H2O2 (P < 0.001), but was ineffective if added simultaneously with H2O2 (P = not significant). (B) Myocytes exposed to a xanthine/xanthine oxidase system were treated for 6 hr with simultaneous administration of 50 μM deferoxamine, 20 μM iron-loaded exochelin 784SM (Fe-EXO), 20 μM desferri-exochelin 784SM (D-EXO), or control medium. The desferri-exochelin markedly reduced cell injury (P < 0.001), but deferoxamine and the iron-loaded exochelin had no effect (P = not significant) (n = 3).