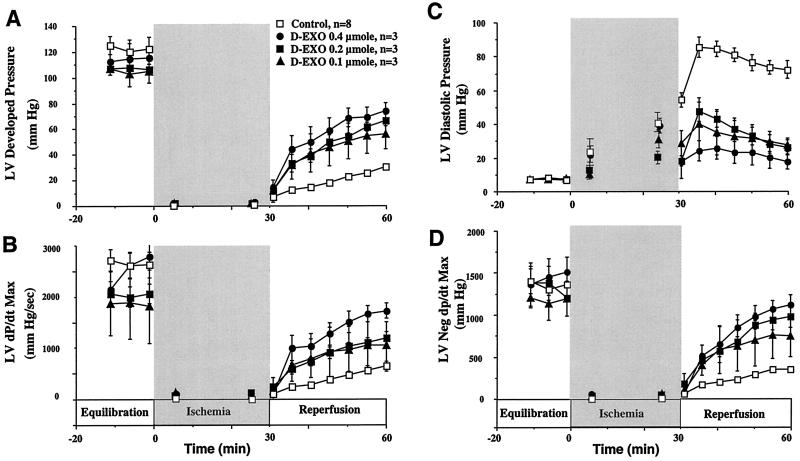
Figure 4.
Desferri-exochelins protect against cardiac reperfusion injury. Adult rabbit hearts were perfused by a nonrecirculating Langendorff technique with ventricular pacing. The hearts were subjected to 30 min of hypoxia followed by 30 min of reperfusion with oxygenated buffer. Mixtures of desferri-exochelins in saline (770SM, 772SM, 784SM, and 798TM) in doses of 0.1, 0.2, or 0.4 μmol, resulting in concentrations of approximately 1, 2, and 4 μM, (n = 3 for each dose) were injected into the root of the aorta during the first 2 min of reperfusion; the control group (n = 6) received saline. Values are mean ± standard error. In hearts treated with desferri-exochelins there was a dose-dependent improvement in two indices of left ventricular systolic function, developed pressure and dP/dt Max, during reperfusion (A and B) (P < 0.001 for each by repeated measures ANOVA). In addition, desferri-exochelins attenuated the deleterious elevation in left ventricular diastolic pressure during reperfusion (C) and improved (increased) another index of diastolic dysfunction, maximum negative dP/dt, in a dose-dependent manner (D) (P < 0.001 for each).