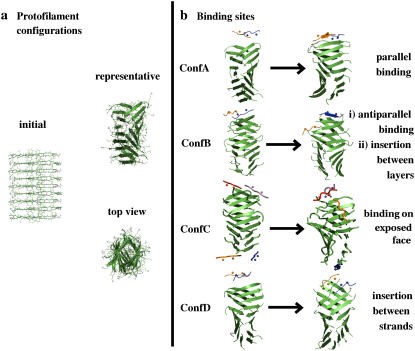
FIGURE 5.
(a) Initial structure of the model protofilament generated by translations and rotations of a single β-strand of Aβ16–22 (Ace-Lys16 Leu17 Val18 Phe19 Phe20 Ala21 Glu22 -NH2). (b) Snapshots at 50 ns indicate four possible scenarios for Aβ16−20m peptide binding to the Aβ16−22 protofilament. In ConfA and ConfB the inhibitor binds at the edge of the protofilament via hydrogen-bond formation in either parallel or antiparallel relative orientation to the edge strand; the other inhibitor molecule shown in ConfB drifts from the edge to the lateral side of the protofilament and intercalates in between the layers; in ConfC one inhibitor binds to one of the solvent-exposed protofilament faces and across several strands of the protofilament, with N-methyl groups facing the protofilament; in ConfD, two inhibitors interact with an edge strand breaking the symmetry between protofilament layers. Animations illustrating the different binding sites are shown in the Supplementary Material.