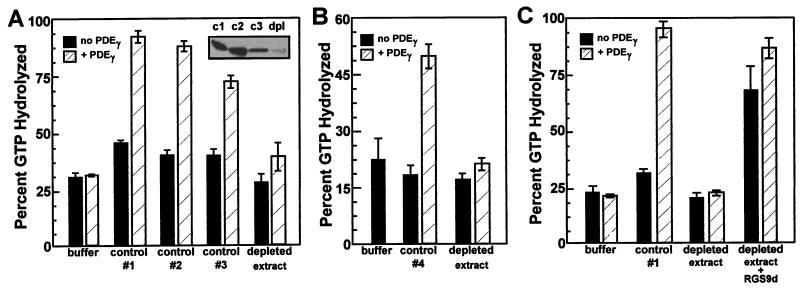
Figure 3.
Removal of ROS GAP activity by immunodepletion of RGS9. (A) RGS9 antibodies were immobilized on protein A-Sepharose and incubated with OG-solubilized ROS as described in the text. After removal by centrifugation, the ROS supernatants were analyzed for ROS GAP activity, PDEγ-enhanced ROS GAP activity, and RGS9 protein remaining in the supernatant (immunoblot, inset). Control samples are: 1, solubilized ROS extract; 2, solubilized extract after incubation with immobilized pre-immune rabbit antibodies; and 3, solubilized extract after incubation with RGS9 antibodies, which had been pre-incubated with recombinant RGS9 bound to Ni2+-NTA agarose prior to immobilization on protein A-Sepharose. Depleted extract, solubilized ROS extract after incubation with RGS9 antibodies, which had been pre-incubated with Ni2+-NTA agarose only prior to immobilization on protein A-agarose. For assays containing PDEγ (hatched boxes), a final concentration of 1.84 μM was used. (B) Immunodepletion by directly coupled antibodies. Either CNBr-activated Sepharose 4B with covalently coupled purified RGS9 antibodies or rabbit IgG-agarose was incubated with OG-solubilized ROS (control 4), and the supernatants were assayed for PDEγ-enhanced ROS GAP activity. PDEγ (hatched boxes) was present at 1.17 μM. (C) Extract was immunodepleted as in A, without preincubation of IgG with Ni2+-NTA agarose, and recombinant RGS9d (6) was added (10 μM) with or without PDEγ (0.3 μM). Control #1 is as in A.