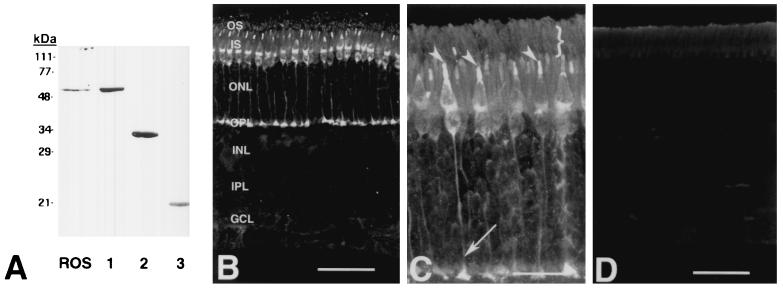
Figure 4.
Immunolocalization of RGS9 in bovine retina by monoclonal antibody. (A) RGS9 immunoblot showing labeling of RGS9 from bovine ROS and full-length and truncated forms of bacterially expressed RGS9. ROS, bovine ROS (20 μg rhodopsin). Lane 1, His-RGS9 (delta30N, 0.6 μg) corresponding to aa 31–484. Lane 2, His-RGS9c (0.6 μg) corresponding to aa 226–484. Lane 3, His-RGS9d (0.6 μg) corresponding to aa 291–418. (B–D) Confocal immunolocalization. RGS9 immunolabeling (B and C) is present in rod and cone photoreceptors. These sensory neurons extend from the outer segment layer (OS) to the outer plexiform layer (OPL) where their axons terminate. Antibody labeling is more prominent in the cones, whose cell soma are adjacent to the IS layer, in the outer most tier of the outer nuclear layer (ONL). Antibody labeling was not observed in the inner nuclear layer (INL), inner plexiform layer (IPL), or ganglion cell layer (GCL). At higher magnification (C), the subcellular distribution of RGS9 in rods and cones is demonstrated. Cone OS are heavily labeled (arrowheads), whereas rod OS (}) are less intensely labeled. Rod and cone IS are also RGS9 immunopositive, although labeling is more pronounced in the cones. Cone photoreceptors terminate in the OPL where their axons form synaptic terminals. Cone axons and synaptic terminals (arrow) are positive for RGS9. (D) RGS9 immunolabeling is abolished by preadsorbing the antibody with purified RGS9 protein coupled to CNBr-activated Sepharose. Scale bars are 50 μm in B and D and 20 μm in C.