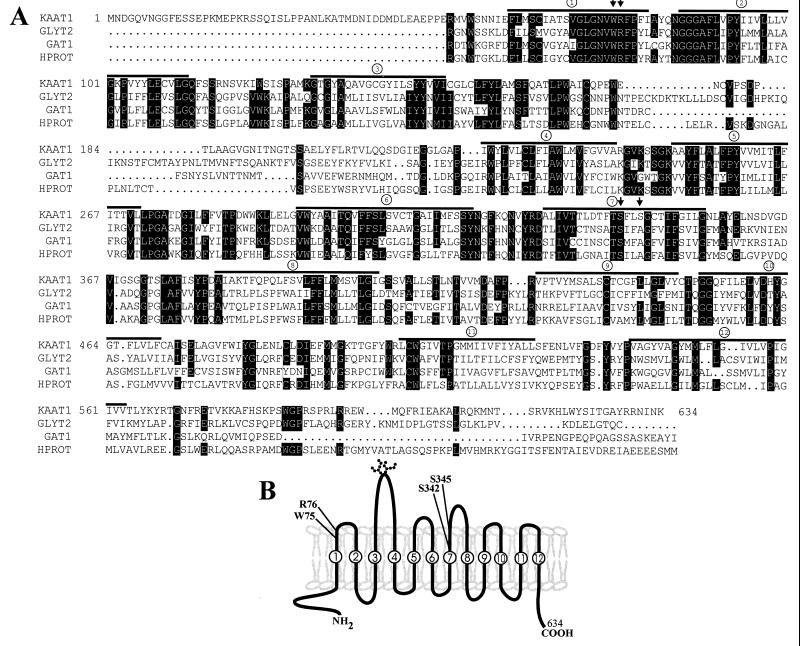
Figure 2.
(A) Deduced amino acid sequence of KAAT1 cDNA and alignment with sequences of members of the Na+-Cl−-dependent GABA transporter family: glycine transporter GLYT2 from rat, GABA transporter GAT1 from rat, and brain specific l-proline transporter (HPROT) from human. Putative transmembrane domains are underlined, and residues considered to be critical for function are highlighted by vertical arrows (see below). (B) Hypothetical secondary structure of KAAT1 based on Kyte–Doolittle analysis. Two putative N-glycosylation sites are indicated between transmembrane domains 3 and 4. Residues marked are those considered to be functionally important based on the following observations: mutagenesis of GAT1 suggested that tryptophan 75 and arginine 76 (KAAT1 numbering) are involved in Na+ and Cl− binding, respectively (25). In the dopamine transporter, it was hypothesized that S342 and S345 (KAAT1 numbering) represent the binding site for dopamine’s hydroxyl group (26).