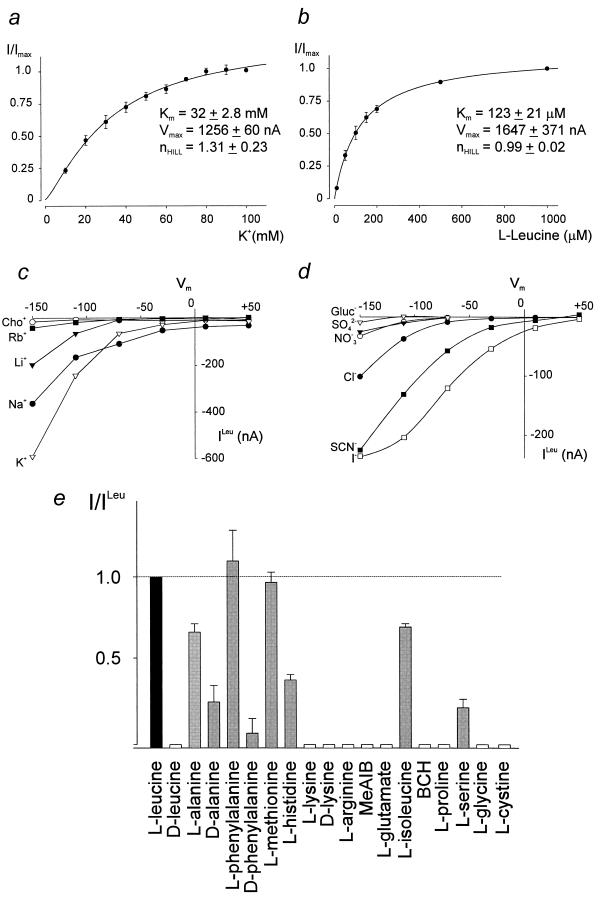
Figure 3.
(a and b) External K+ and leucine concentration dependence of KAAT1-evoked uptake currents. Data are steady-state currents obtained at −150 mV by using a voltage jump protocol that steps the membrane potential to −150 mV for 100 ms from a holding potential of −50 mV. Data points (mean ± SEM, n = 3) were normalized against the maximal current from the same oocyte and fitted by least-squares according to the equation: I/Imax = [S]n/{[S]n + Kn0.5}. (c and d) Cation and anion dependency of KAAT1-mediated leucine uptake. The figure shows steady-state current-voltage relations of a representative oocyte between +50 and −150 mV, obtained by subtraction of control currents from the corresponding currents in the presence of 200 μM leucine. (e) Substrate specificity of KAAT1. An oocyte expressing KAAT1 was held at −50 mV in the uptake solution containing 100 mM KCl, and specific substrates were applied at 200 μM concentration. Data represent the mean ± SEM of three separate experiments and were normalized against the uptake current induced by 200 μM l-leucine.