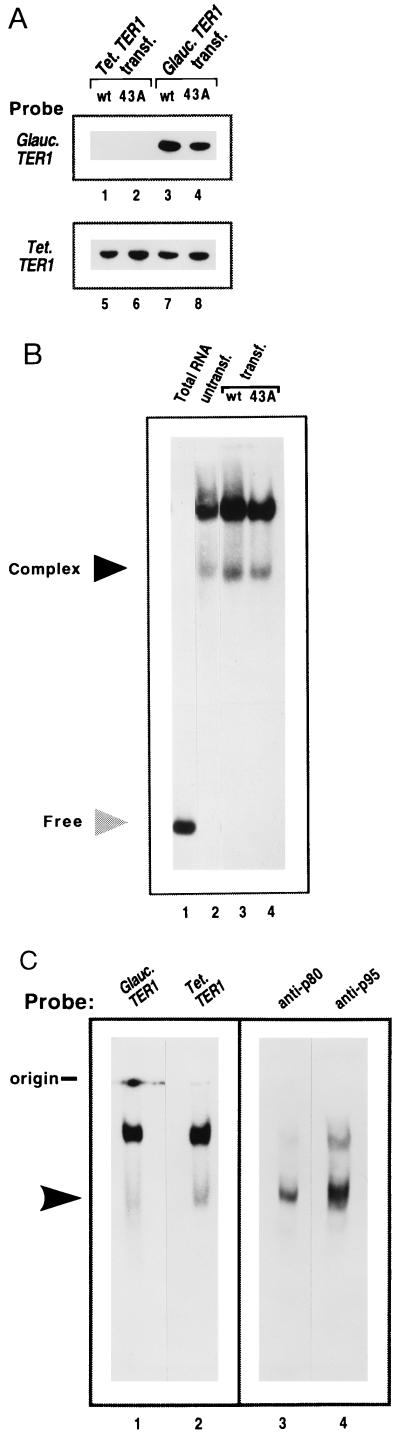
Figure 2.
Heterologous expression and assembly of Glaucoma telomerase RNA into an RNP complex. (A) Northern blot analysis of Tetrahymena transformants expressing the Gc.TER1 gene in vivo. Total RNA from Tetrahymena or Glaucoma TER1 or ter1–43A transformants was fractionated on denaturing gels. Blots probed with a Gc.TER1-specific gene probe (lanes 1–4) revealed presence of Gc.TER1 RNA in vivo (lanes 3 and 4). Blots were reprobed with a Tt.TER1-specific probe (lanes 5–8); endogenous Tetrahymena TER1 RNA was observed in Gc.TER1 and Gc.ter1–43A transformants (lanes 7 and 8). (B) Assembly of Tetrahymena TER1 RNA into a telomerase RNP complex. RNP complexes prepared from untransformed, vegetative Tetrahymena cells (lane 2) and Tt.TER1 or Tt.ter1–43A transformants (lanes 3 and 4) were studied by RNP gel analysis; blots were probed with a Tetrahymena TER1-specific probe (see Methods). Lane 1 contains total RNA (≈10 μg) prepared from Tt.TER1 transformants. Light shaded arrow indicates free telomerase RNA, and dark arrow indicates lower putative telomerase RNP complex. (C) Identity of RNP complexes in Gc.ter1–43A transformants. RNP complexes from Gc.ter1–43A transformants were analyzed by sequentially probing with a Gc.TER1-specific probe (lane 1) and then a Tt.TER1-specific probe (lane 2). Lanes 3 and 4 are duplicate loadings subjected to Western blot analysis using telomerase anti-p80 and -p95 antibodies, respectively. Arrow identifies lower RNP complex.