Abstract
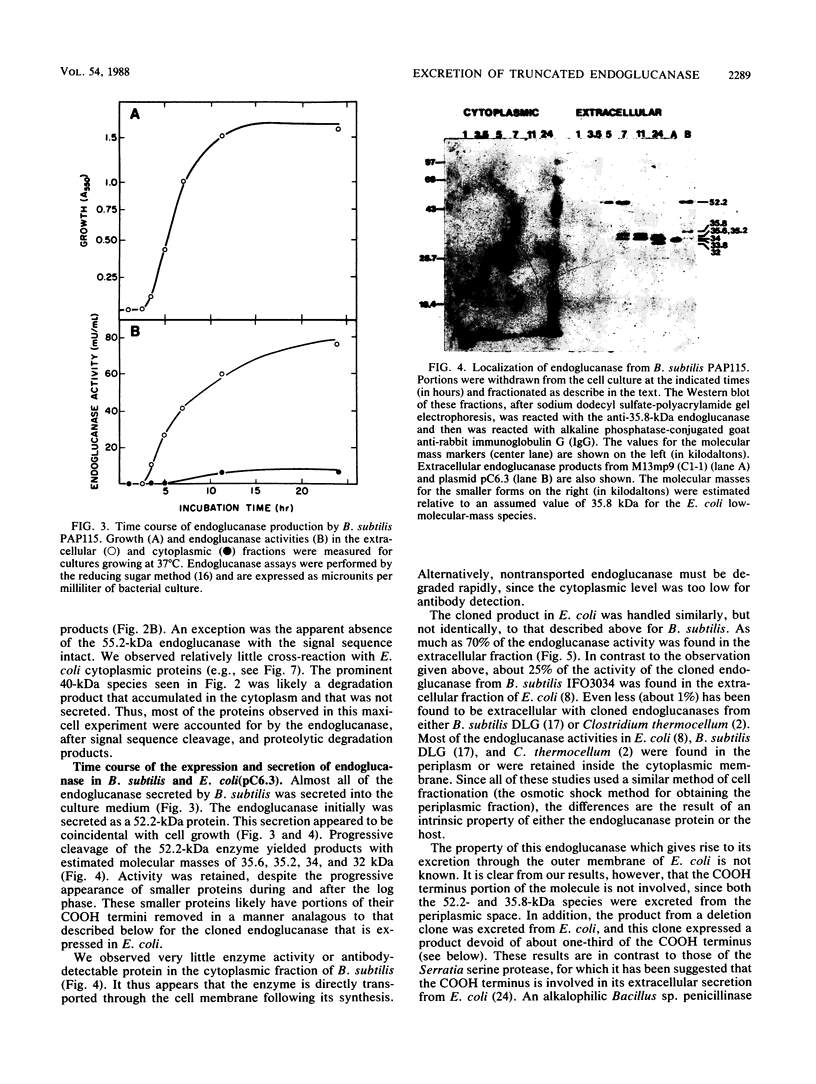
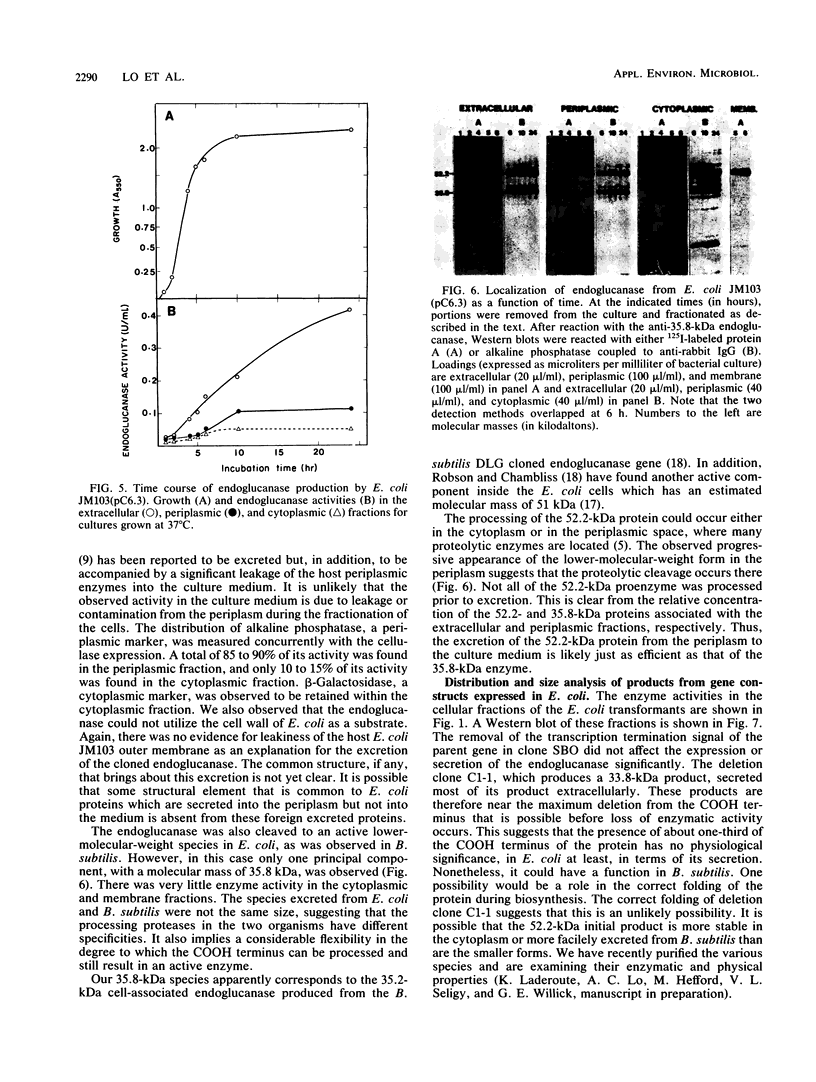
We compared the secretion of a Bacillus subtilis endo-β-1,4-glucanase (EC 3.2.1.4) in B. subtilis and of the product from the cloned gene (pC6.3) expressed in Escherichia coli. The cloned enzyme has been isolated previously as the 52.2-kilodalton (kDa) species predicted from the gene sequence (R. M. MacKay, A. Lo, G. Willick, M. Zuker, S. Baird, M. Dove, F. Moranelli, and V. Seligy, Nucleic Acids Res., 14:9159-9170, 1986); this 52.2-kDa species is then converted to an active 35.8-kDa species. The 35.8-kDa species has a segment removed from the COOH terminus. Endoglucanase products were identified by use of an antibody directed to the 35.8-kDa enzyme. Time course studies of the secretion in B. subtilis showed that the enzyme was first secreted as a 52.2-kDa proenzyme. This was cleaved progressively to a product of about 32 kDa. Time course analysis of the expression of the cloned product from pC6.3 in E. coli showed that about 70% of the endoglucanase activity was found extracellularly. Analysis of active products from three deletion clones showed that the expression pattern of the endoglucanase was not affected by removal of the transcription termination signal and that neither expression nor secretion was substantially altered by removal of a region coding for up to 163 residues of the carboxyl terminus.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cornelis P., Digneffe C., Willemot K. Cloning and expression of a Bacillus coagulans amylase gene in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(4):507–511. doi: 10.1007/BF00337957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Hall M. N., Silhavy T. J. A mechanism of protein localization: the signal hypothesis and bacteria. J Cell Biol. 1980 Sep;86(3):701–711. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.3.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo T., Kato C., Horikoshi K. Excretion of the penicillinase of an alkalophilic Bacillus sp. through the Escherichia coli outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):949–951. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.949-951.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay R. M., Lo A., Willick G., Zuker M., Baird S., Dove M., Moranelli F., Seligy V. Structure of a Bacillus subtilis endo-beta-1,4-glucanase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):9159–9170. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.9159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson L. M., Chambliss G. H. Cloning of the Bacillus subtilis DLG beta-1,4-glucanase gene and its expression in Escherichia coli and B. subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):612–619. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.612-619.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson L. M., Chambliss G. H. Endo-beta-1,4-glucanase gene of Bacillus subtilis DLG. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2017–2025. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2017-2025.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J., Barrett K. The reversible dissociation of the alkaline phosphatase of Escherichia coli. I. Formation and reactivation of subunits. J Biol Chem. 1965 Nov;240(11):4284–4292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worcel A., Burgi E. Properties of a membrane-attached form of the folded chromosome of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 5;82(1):91–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90576-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagida N., Uozumi T., Beppu T. Specific excretion of Serratia marcescens protease through the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):937–944. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.937-944.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]