Figure 1.
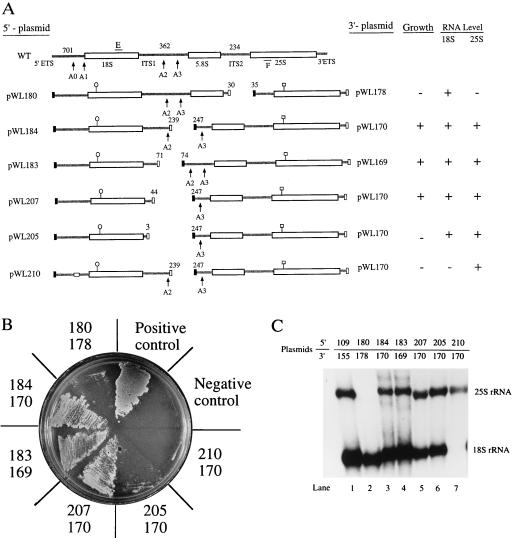
The large rDNA operon of S. cerevisiae can be successfully expressed in two parts. (A) Expression of small and large subunit rRNAs in trans. The yeast rDNA operon was divided at the sites indicated, and each segment was expressed from a different plasmid, under control of GAL7 promoters and terminators (closed and open boxes). The experimental 18S and 25S RNA coding units contained unique hybridization tags (○| and □|) and the plasmids harboring the 5′ and 3′ portions of the operon carried URA3 and TRP1 genes (see Materials and Methods). rDNA function was evaluated in yeast strain NOY504, which contains a ts RNA polymerase I mutation and mutations in URA3 and TRP1 (7). Plasmid pWL210 is identical to pWL184 except that it contains a 6-nt substitution in the 5′ ETS region (open rectangle) shown to base-pair with U3 snoRNA (472AAAGAG477→UCUUCA; ref. 8). Sites of pre-rRNA processing (A0, A1, etc.) are indicated by arrows. Sizes of the ETS and ITS segments are shown above the wild-type operon. E and F refer to sites used to prime PCR amplification. Growth and RNA levels are indicated at the right. The numbers above the experimental constructs refer to the nucleotide positions at which they were divided. Note that the dissections are imperfect, with at least a few nucleotides absent in each case (see also Fig. 2). (B) Phenotypic properties of the split operons. Transformants containing the plasmid pairs shown in A were streaked on galactose plates at 37°C and incubated for 7 days. The positive control contained a pair of plasmids with intact rDNA operons (pWL109 and pWL155), and the negative control contained vectors without rDNA inserts. Growth phenotypes are summarized in A. +, good growth (colonies evident in 7 days); −, no growth. (C) Northern hybridization analysis of rRNA expressed in trans. Cells were first grown in glucose medium at 25°C and then diluted into galactose medium. RNA was extracted after incubation at 37°C for 7 h (9). Northern assays were carried out using probes specific for unique hybridization tags in 18S and 25S RNAs. Plasmids pWL109 and pWL155 were used as a positive control. The levels of 18S and 25S RNAs are tabulated in A; + indicates wild-type level, and − indicates an undetectable level.