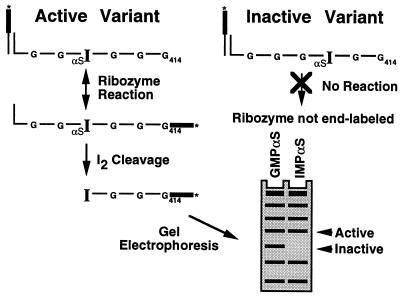
Figure 2.
Scheme for the identification of the chemical groups important for RNA activity by NAIM. In this example, IMPαS is randomly incorporated in place of G at a low ratio into the L-21 G414 RNA. Active variants covalently transfer the 3′ end of the exon onto the 3′ terminus of the intron. Hydrolysis of the phosphorothioate linkage with iodine breaks the RNA at the sites of IMPαS incorporation. Separation of the cleavage fragments by PAGE produces a sequencing ladder that represents the sites tolerant of IMPαS substitution. In contrast, inactive variants fail to react with the oligonucleotide which leaves a gap in the sequencing ladder. RNAs containing GMPαS are tested to insure that loss of activity is not due to the phosphorothioate group used to chemically tag the inosine.