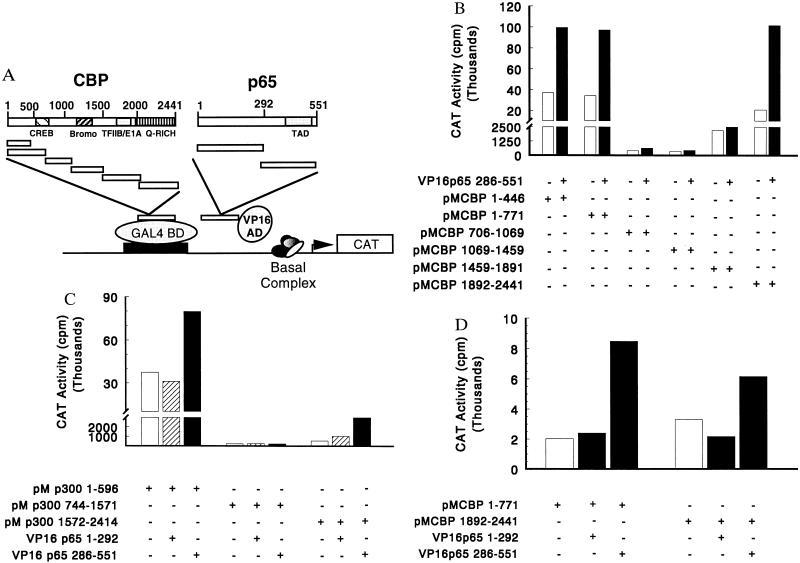
Figure 3.
CBP/p300 and p65 functionally interact in a mammalian two-hybrid system. (A) Structures of the CBP-GAL4 and p65 VP16 constructs. The indicated regions of CBP were cloned into a vector (pM) containing the GAL4 DNA binding domain (BD). Similarly, overlapping regions of p65 were inserted into a vector containing the VP16 activation domain (AD). (B) The N and C termini of CBP interact with the C terminus of p65. COS cells were cotransfected with 2 μg of the pG5CAT reporter gene, 10 μg of the indicated GAL4(pM), and 10 μg of VP16 expression plasmids. Total DNA was kept constant at 22 μg. Data are representative of five experiments. When pooled data were analyzed by the nonparametric Wilcoxon signed rank test, the CBP 1–771 versus CBP 1–771 and p65 286–551 were significantly different (P = 0.015), as were the CBP 1892–2441 versus CBP 1892–2441 and p65 286–551 (P = 0.031). (C) The N and C termini of p300 interact with the C terminus of p65. Cells were cotransfected as described above (B). Data are representative of five experiments. (D) The C terminus of p65 containing the transcriptional activation domain is required for interaction with either the N or C terminus of CBP. Cells were cotransfected as above (B). Data are representative of three experiments.