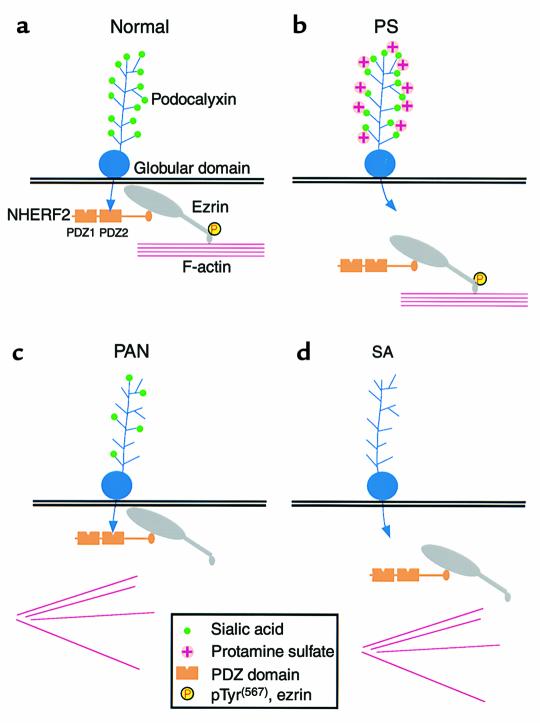
Figure 10.
Models for the sites of disruption of the PC/NHERF2/ezrin complex with the actin cytoskeleton in pathological conditions associated with changes in foot process organization. (a) Normal glomerulus. PC binds to the second PDZ domain (PDZ2) of NHERF2 through its C-terminal PDZ-binding motif along the apical region of GECs. NHERF2 binds to the N-terminus of phosphorylated (unmasked) ezrin through its C-terminal ERM-binding region. Unmasked phosphorylated (P) ezrin links the complex to the actin cytoskeleton through its C-terminal actin-binding site. (b) Protamine sulfate (PS) treatment. Neutralization of the negative charge on the extracellular domain of PC by PS disrupts the binding of the cytoplasmic tail of PC to NHERF2. (c) PAN (10d) treatment. The PC/NHERF2/ezrin complex remains intact, but ezrin dissociates from the actin cytoskeleton with a concomitant decrease in the level of phosphorylated ezrin. (d) Sialidase (SA) treatment. When sialic acid is removed from PC by SA digestion, the complex is disrupted in two places: PC dissociates from NHERF2 and ezrin dissociates from the actin cytoskeleton with a concomitant reduction in the level of phosphorylated ezrin.