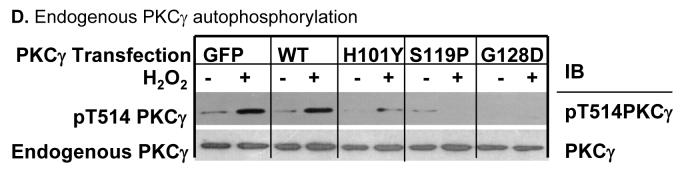
Figure 2. PKCγ C1B mutations alter endogenous PKCγ activity.
Stably-transfected N/N1003A lens epithelial cells were treated with 100 μM H2O2 for 20 min. After that cells were harvested. The whole cell extracts were used to immunoprecipitate either the EGFP-tagged wild type PKCγ or C1B mutants by anti-GFP antibodies (A), or both endogenous PKCγ and EGFP tagged PKCγ or mutants by anti-PKCγ antibodies (B). The precipitates were used for the enzyme sources to determine enzyme activity as described. As a loading control, total immunoprecipitated wild type PKCγ (endogenous and/or EGFP-tagged) or C1B mutant proteins were shown by Western blot (inserted panels). PKCγ enzyme activity was expressed as % of the activity of untreated wild type PKCγ with GFP tags. The enzyme activity was normalized by calibration of the relative level of phosphorylated substrates to the relative amount of PKCγ:EGFP or wild type PKCγ + PKCγ:EGFP in the immunoprecipitation as determined by Western blotting. * indicates significant increases in PKCγ enzyme activities compared to levels in control cells with overexpression of wild type PKCγ only (A) or with both endogenous and exogenous wild type PKCγ (B). Same whole cell extracts were used to detect the phosphorylation of PKCγ on Thr514 by Western blot using anti-phospho-Thr514 PKCγ as a probe. Phospho-Thr514 PKCγ:EGFP or mutants are shown (C). Total PKCγ:EGFP protein levels were revealed as loading controls (C, lower panel). H2O2-induced autophosphorylation of endogenous PKCγ on Thr514 in cells overexpressing EGFP tag, wild type PKCγ, or PKCγ C1B mutants are shown (D). Endogenous wild type PKCγ protein levels were revealed as loading controls (D, lower panel).