Figure 1.
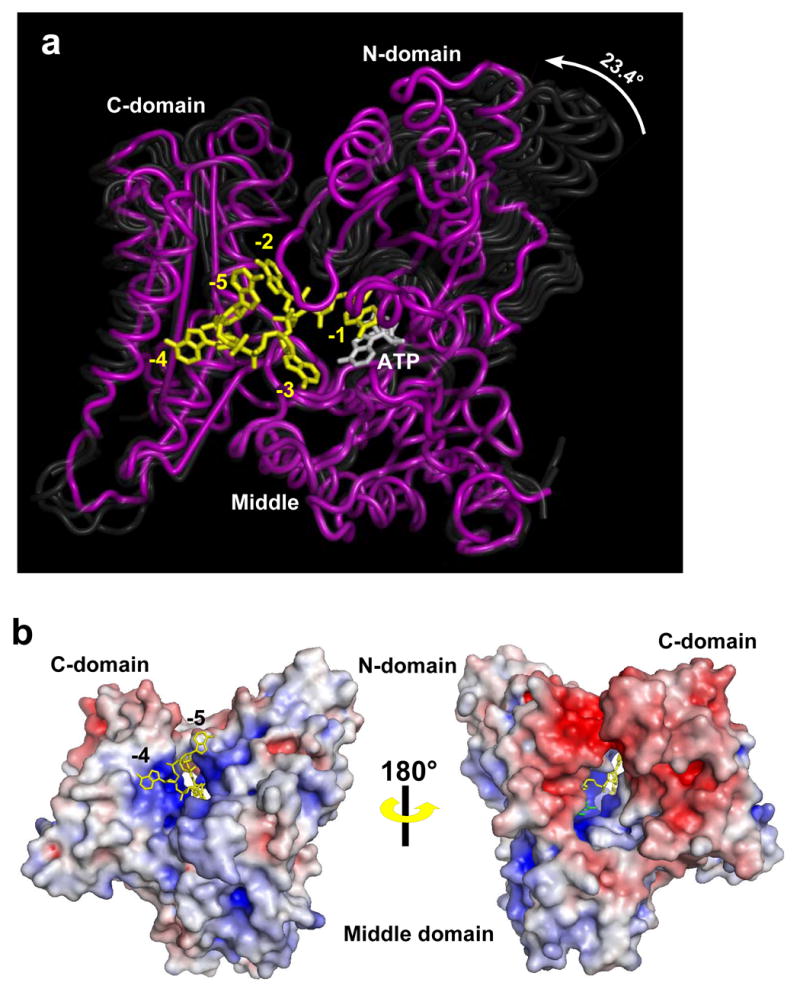
Structure of PAP in complex with ATP and RNA. (A) The structure of the closed, ternary complex of PAP is shown in purple, and ATP and RNA are shown in white and yellow, respectively. The middle domains of the earlier PAP structures have all been superimposed with that of the ternary complex, and the earlier structures are shown as transparent ghosts to highlight the domain movements. (B). Two views of the surface representations of the PAP/ATP/RNA complex are shown. The color reflects the surface electrostatics where the color gradient from red to white to blue corresponds to −8KT to 0 KT to +8KT. The top view is rotated ~45 degrees relative to that shown in 1A. The -5 and -4, RNA nucleotides (yellow) are seen exiting a cleft formed by the three domains. The bottom view has been rotated ~180 about the vertical axis relative to the top, so that the ATP-binding side of the active site cleft is visible. Part of the ATP base (green) and the -2 nucleotide (yellow) are seen. The nucleotide at the 3′ end is hidden within the active site cavity.
