Abstract
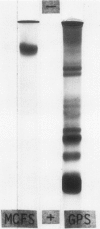
A macrophage-chemotactic factor (MCFS) was extracted in the pseudoglobulin fraction from delayed hypersensitivity skin lesions induced by bovine gamma-globulin in guinea pigs. Its chemotactic activity was estimated by a modification of Boyden's method using Nuclepore filter. After chromatography of the protein fraction using Sephadex G-50 and DEAE-cellulose, in that order, two chemotactic fractions were obtained. The chemotactic factor with stronger activity (MCFS-1) was further highly purified (488-fold) by chromatography on CM-Sephadex. This factor migrated in a single band on acrylamide disc gel electrophoresis and was found to be a protein that was free of nucleic acid. Gel filtration showed that its molecular weight was similar to that of IgG. Its chemotactic activity was heat labile. Intradermal injection of this factor into normal guinea pigs induced a pronounced mononuclear cell emigration from venules. These findings are pertinent to understanding macrophage reaction in the delayed hypersensitivity reactions. Am J Pathol 87:359-374, 1977).
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman L. C., Kirchner H. Mononuclear leucocyte chemotaxis in the chicken. Definition of a phylogenetically specific lymphokine. Immunology. 1974 Feb;26(2):393–405. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman L. C., Snyderman R., Oppenheim J. J., Mergenhagen S. E. A human mononuclear leukocyte chemotactic factor: characterization, specificity and kinetics of production by homologous leukocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):801–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYDEN S. The chemotactic effect of mixtures of antibody and antigen on polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Exp Med. 1962 Mar 1;115:453–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.3.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Ward P. A., Yoshida T., Burek C. L. Biologic activity of extracts of delayed hypersensitivity skin reaction sites. Cell Immunol. 1973 Dec;9(3):363–376. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausman M. S., Snyderman R., Mergenhagen S. E. Humoral mediators of chemotaxis of mononuclear leukocytes. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jun;125(6):595–602. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.6.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirashima M., Honda M., Hayashi H. The mediation of tissue eosinophilia in hypersensitivity reactions. II. Separation of a delayed eosinophil chemotactic factor from macrophage chemotactic factors. Immunology. 1976 Aug;31(2):263–271. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz D. A., Garrett M. A. Use of leukocyte chemotaxis in vitro to assay mediators generated by immune reactions. I. Quantitation of mononuclear and polymorphonuclear leukocyte chemotaxis with polycarbonate (nuclepore) filters. J Immunol. 1971 Mar;106(3):649–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kambara T., Katsuya H., Maeda S. Experimental study on the mechanisms of delayed hypersensitivity reaction, with special reference to emigration and function of mononuclear cells. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1972 Aug;22(3):465–476. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1972.tb01845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYASHI H., MIYOSHI H., NITTA R., UDAKA K. Proteolytic mechanism in recurrence of Arthus-type inflammation by thiol compounds. Br J Exp Pathol. 1962 Oct;43:564–573. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda S., Yoshinaga M., Hayashi H. Characterization of a chemotactic factor (leucoegresin) for polymorphonuclear leucocytes from thermal skin site. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1975 Sep 29;19(1):37–49. doi: 10.1007/BF02889354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meacock S. C., Willoughby D. A. Purification of serum proteins from lymph node cell extracts with permeability activity characteristic of the lymph node permeability factor. Immunology. 1968 Jul;15(1):101–113. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiura M., Matsumura K., Hayashi H. The natural mediator for PMN emigration in inflammation. VIII. Production of leucoegresin-like chemotactic factor in reversed passive Arthus reactions in rats. Immunology. 1976 Apr;30(4):521–527. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORNSTEIN L. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. I. BACKGROUND AND THEORY. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:321–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POSTLETHWAITE A. E., Snyderman R. Characterization of chemotactic activity produced in vivo by a cell-mediated immune reaction in the guinea pig. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):274–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postlethwaite A. E., Kang A. H. Collagen-and collagen peptide-induced chemotaxis of human blood monocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1299–1307. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Altman L. C., Hausman M. S., Mergenhagen S. E. Human mononuclear leukocyte chemotaxis: a quantitative assay for humoral and cellular chemotactic factors. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):857–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Shin H. S., Hausman M. H. A chemotactic factor for mononuclear leukocytes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Nov;138(2):387–390. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-35903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Shin H., Dannenberg A. M., Jr Macrophage proteinase and inflammation: the production of chemotactic activity from the fifth complement by macrophage proteinase. J Immunol. 1972 Oct;109(4):896–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhr J. W. Delayed hypersensitivity. Physiol Rev. 1966 Jul;46(3):359–419. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1966.46.3.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLOUGHBY D. A., SPECTOR W. G., BOUGHTON B. A LYMPH-NODE PERMEABILITY FACTOR IN THE TUBERCULIN REACTION. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1964 Apr;87:353–363. doi: 10.1002/path.1700870216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Altman L. C., Oppenheim J. J., Mergenhagen S. E. In vitro studies of a chemotactic lymphokine in the guinea pig. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1974;46(5):768–784. doi: 10.1159/000231176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A. Chemotoxis of mononuclear cells. J Exp Med. 1968 Nov 1;128(5):1201–1221. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.5.1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Remold H. G., David J. R. The production by antigen-stimulated lymphocytes of a leukotactic factor distinct from migration inhibitory factor. Cell Immunol. 1970 Jul;1(2):162–174. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Yoshinaga M., Hayashi H. The natural mediator for PMN emigration in inflammation. II. Common antigenicity of leucoegresin with immunoglobulin G. Immunology. 1971 May;20(5):803–808. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yammoto S., Nishiura M., Hayashi H. The natural mediator for PMN emigration in inflammation. V. The site of structural change in the chemotactic generation of immunoglobulin G by inflammatory SH-dependent protease. Immunology. 1973 May;24(5):791–801. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Yoshinaga M., Hayashi H. Leukoegresin: a factor from rabbit skin associated with leucocytic emigration in the Arthus reaction. Nature. 1968 Jun 8;218(5145):977–978. doi: 10.1038/218977b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaga M., Yamamoto S., Maeda S., Hayashi H. The natural mediator for PMN emigration in inflammation. 3. In vitro production of a chemotactic factor by inflammatory SH-dependent protease from serum immunoglobulin G. Immunology. 1971 May;20(5):809–815. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaga M., Yoshida K., Tashiro A., Hayashi H. The natural mediator for PMN emigration in inflammation. I. Purification and characterization of leucoegresin from Arthus skin site. Immunology. 1971 Aug;21(2):281–298. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]