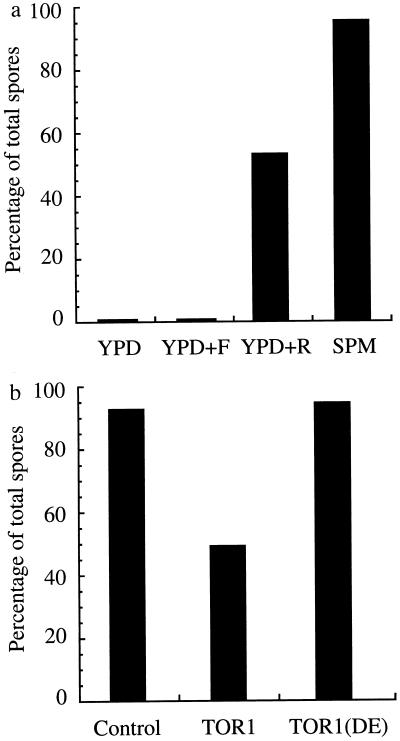
Figure 2.
(a) Rapamycin induces SK-1 cells to sporulate in saturated YPD culture. Diploid SK-1 cells were incubated in YPD for 24 hr at 30°C with vigorous shaking. The cells reached saturation and arrested in G1. The cell culture was equally divided into three aliquots. Each aliquot was incubated with methanol (control), 100 nM FK506 (YPD + FK506), or 100 nM rapamycin (YPD + rapamycin). As a positive control, the same saturated SK-1 cell culture in YPD was diluted 1:50 into YPA and incubated for 13.5 hr. The cells were washed with sterile water, resuspended into SPM, and incubated for another 13 hr. The proportion of total sporulated cells was calculated as in Fig. 1a (average of three experiments, n = 250). (b) Overexpression of plasmid-borne wild-type, but not the kinase-inactive mutant TOR1, partially blocks sporulation. The diploid SK-1 cells carrying pGAL1 alone, pGAL1-TOR1, or pGAL1-TOR1 (Asp-2294 → Glu) were incubated in complete synthetic medium-Leu-Glu for 36 hr at 30°C with vigorous shaking, washed twice in sterile water, and resuspended into the 50 vol of YPA for another 10 hr. Galactose (0.1%) was added to the culture. The cells were incubated for another 3.5 hr during protein induction, then washed twice with sterile water, resuspended in SPM containing 0.1% galactose, and incubated for 13 hr. The samples were analyzed as in a (average of three experiments, n = 250).