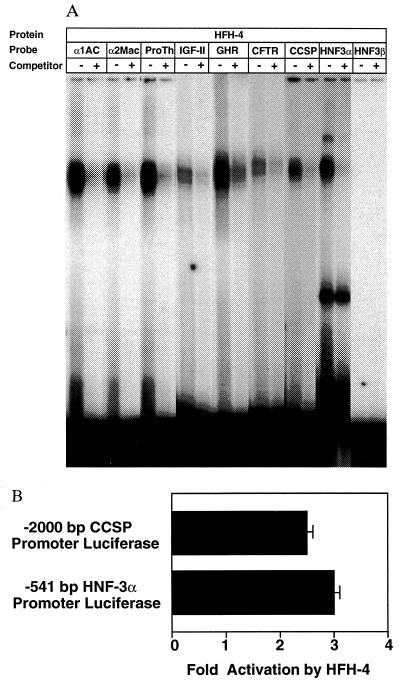
Figure 4.
Identification of potential HFH-4 target genes. (A) DNA-binding assays with recombinant HFH-4 protein and potential HFH-4-binding sites in target genes of the choroid plexus and bronchiolar epithelium. EMSA with labeled HFH-4-binding site oligonucleotides (1 ng) and recombinant GST-HFH-4 winged helix protein (60 ng; see Table 3 for sequences). Competitions included a 200-fold molar excess of unlabeled oligonucleotides in the binding reaction. α2MAC, α2-macroglobulin; ProTh, prothrombin; and GHR, growth hormone receptor. Note that the HFH-4-binding sequence in the promoter of the prothrombin gene is identical to that of the βAPP gene (Table 3). (B) Cotransfection assays demonstrate HFH-4 transcriptional activation of putative target promoters. The CMV-HFH-4 expression vector was cotransfected with the −541 rat HNF-3α and the −2000 rat CCSP promoter luciferase plasmids in HepG2 cells and analyzed for luciferase enzyme activity. Shown is the normalized fold promoter activation by the CMV-HFH-4 expression vector compared with the CMV plasmid and the error bars represent the SD from three separate experiments. The −431 rat HNF-3α promoter construct, which lacks the HFH-4-binding site, was not activated by HFH-4.