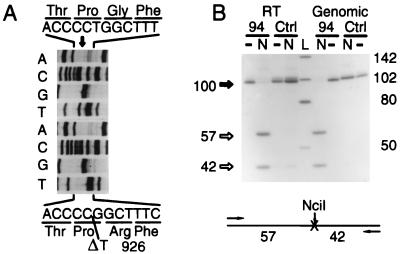
Figure 3.
Mutations in the XPG gene of patient 94RD27. (A) Sequence of wild-type (top) and 94RD27 (bottom) RT-PCR products showing the T deletion at position 2972. (B) NciI restriction analysis of RT-PCR and genomic PCR products from RD9427 (lanes 94) and a wild-type control (Ctrl). −, Undigested products; N, NciI digests; L, HaeIII digest of pBluescript II-SK+ DNA, with fragment lengths in bp. The T deletion creates a new NciI site (CC/SGG) that is absent from control RNA and DNA. Note that the uncut 94RD27 genomic PCR product is slightly shorter than the control and that it is fully cut by NciI to yield 57-bp and 42-bp fragments.