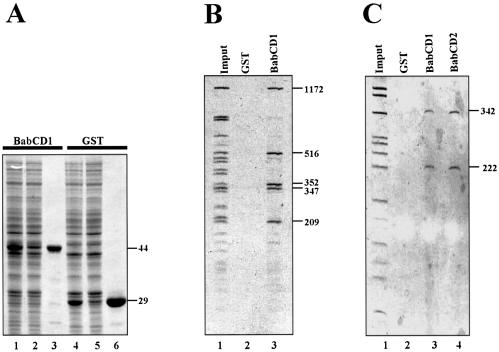
Figure 2.
The BabCD specifically binds to DNA in vitro. (A) GST–BabCD1 fusion protein and GST were produced in E.coli, purified and analyzed by SDS–PAGE electrophoresis, and stained with Coomassie blue. Total protein extracts were analyzed after induction (lanes 1 and 4) or without induction (lanes 2 and 5), and after purification (lanes 3 and 6). The molecular mass of the GST–BabCD1 fusion protein and GST are indicated in kDa on the right. (B) An 8 kb bab1 subclone was digested with HaeIII and the digestion products were incubated with either GST or GST–BabCD1 fusion protein bound to glutathione–agarose beads. The HaeIII digestion products (lane 1) and the fragments retained by GST (lane 2) or GST–BabCD1 (lane 3) were analyzed on 5% polyacrylamide gel. (C) A 2.5 kb bab2 subclone was digested with HaeIII and the digestion products were incubated with either GST, GST–BabCD1 or GST–BabCD2 fusion proteins bound to glutathione–agarose beads. The experiment is as in (B). Lane 1 shows the HaeIII digestion products, lanes 3 and 4 the fragments retained by the GST–BabCD1 and GST–BabCD2 proteins, respectively, and the control experiment with GST is shown in lane 2. The length of the DNA fragments retained by both the GST–BabCD1 and GST–BabCD2 protein are indicated in bp on the right.