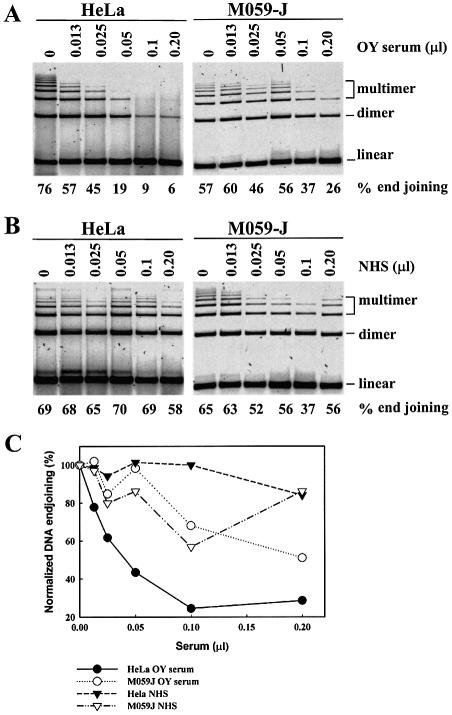
Figure 2.
Serum of polymyositis-scleroderma overlap syndrome patients inhibits in vitro DNA end joining. (A) Twenty micrograms of extract of either HeLa or M059-J cells were incubated in 16 µl of DNA end-joining reaction-mixture (without DNA and ATP) in which 2 µl of serum from OY patient were added, after appropriate dilution in phosphate buffered saline, to achieve the final levels in µl serum per reaction indicated on top of the gel, and were incubated at 25°C for 10 min. After this pre-incubation period, DNA and ATP were added in half of the reaction-mixture to assay for DNA end joining, whereas the remaining reaction-mixture was processed for EMSA (results not shown). Note the inhibition of DNA end joining with increasing serum concentration in reactions assembled with extracts of HeLa cells and the reduced inhibition in reactions assembled with extracts of M059-J cells. (B) Similar to (A), but for reactions assembled in the presence of identical amounts of NHS from a healthy individual. (C) Quantitative evaluation of the DNA end-joining results shown in (A) and (B) using ImageQuant. Results are shown normalized to the percent rejoining measured for each set of reactions when incubated in the absence of serum. Actual values for percent end joining are shown at the bottom of the gels in (A) and (B). Note the inhibition in DNA end joining with increasing amount of OY serum in the reaction, and the difference in the effect between M059-J and HeLa cells, particularly when considering the effect of NHS.