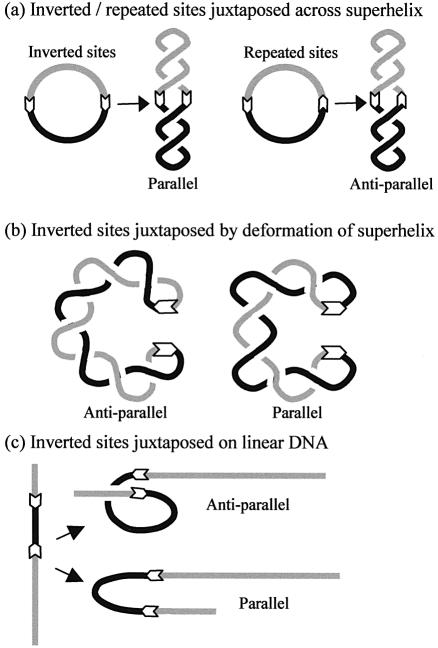
Figure 1.
Juxtapositions of DNA sites. In all cases, white arrows mark the positions (and orientations) of two target sequences in the DNA and black and grey lines the DNA between the targets. (a) When juxtaposed across the superhelical axis, two sites in inverted orientation are aligned in parallel whereas two sites in directly repeated orientation are aligned in an antiparallel manner. (b) When sites in separate segments of the superhelix become juxtaposed by deformations of the superhelix, sites in inverted orientation can give rise to either antiparallel or parallel alignments. (c) In linear DNA, the juxtaposition of two sites in inverted orientation can give rise to either antiparallel or parallel alignments.