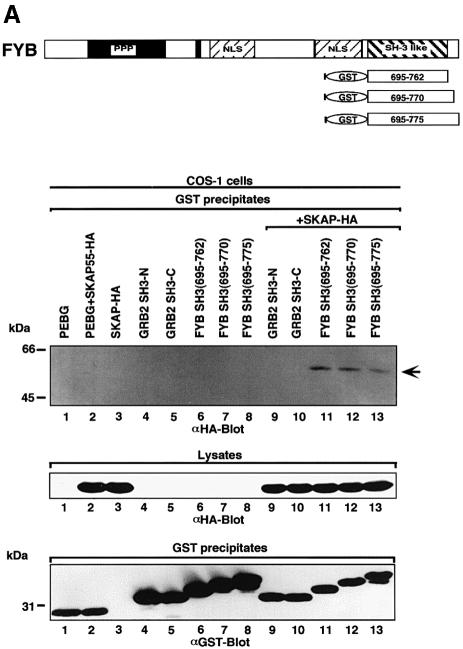
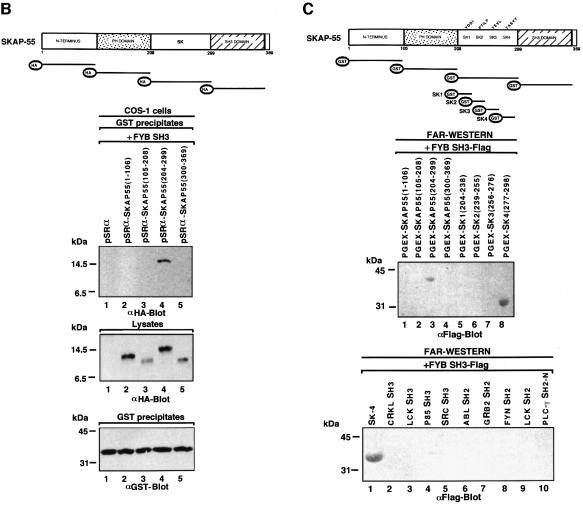
Fig. 1. FYB SH3 domain binding to the SK4 region of SKAP55. (A) The scheme shows mouse full-length FYB, sub-regions and GST–SH3 domain constructs. (Upper panel of gel) FYB SH3 domain binds full-length SKAP55 in COS-1 cells. COS-1 cells were transfected with full-length SKAP55 alone, or with the GRB-2 or various FYB SH3 domain(s) and assessed for complex formation. Glutathione beads were used to precipitate the GST fusion proteins. Lane 1, pEBG; lane 2, pEBG and SKAP55-HA; lane 3, SKAP55-HA; lane 4, GRB-2 N-terminal SH3 domain; lane 5, GRB-2 C-terminal SH3 domain; lane 6, FYB SH3(695–762); lane 7, FYB SH3(695–770); lane 8; FYB SH3(695–775); lane 9, GRB-2 N-terminal SH3 domain and SKAP55-HA; lane 10, GRB-2 C-terminal SH3 domain and SKAP55-HA; lane 11, FYB SH3(695–762) and SKAP55-HA; lane 12, FYB SH3(695–770) and SKAP55-HA; lane 13, FYB SH3(695–775) and SKAP55-HA. The precipitates were separated on a 10% SDS–polyacrylamide gel followed by anti-HA blotting. (Middle panel) Levels of SKAP55 protein expression. As in upper panel, except cell lysate was blotted with anti-HA. (Lower panel) Levels of GST fusion protein expression. As in upper panel, except that precipitates were blotted with anti-GST. (B) Schematic representation of SKAP55 and various sub-regions. Various DNA fragments encoding the SKAP55 were generated by PCR and inserted into the pSRα at the BamHI and KpnI sites with an in-frame HA tag. (Upper panel of gel) In vivo association of FYB SH3 and SKAP55 at SK4 region. COS-1 cells were co-transfected with different GST–SKAP55 subdomains and FYB SH3 domain and assessed for complex formation. Glutathione–Sepharose beads were used to precipitate the GST fusion proteins. Lane 1, pSRαHa plus FYB SH3; lane 2, pSRαHa-SKAP55(1–106) plus FYB SH3; lane 3, pSRαHa SKAP55(105–208) plus FYB SH3; lane 4, pSRαHa-SKAP55(204–299) plus FYB SH3; lane 5, pSRα Ha-SKAP55(300–369) plus FYB SH3. The precipitates were separated on a 10% SDS–polyacrylamide gel and immunoblotted with anti-HA monoclonal antibody. (Middle panel) Levels of FYB protein expression. As in upper panel except that the cell lysate was blotted with anti-HA. (Lower panel) Levels of GST fusion protein expression. As in upper panel except that precipitates were blotted with anti-GST. (C) (Above) In vitro association of FYB SH3 and SKAP55 at SK4 region. The different truncated GST–SKAP55 fusion proteins used in the far-western assay. Lane 1, pGEX-SKAP55(1–106); lane 2, pGEX-SKAP55(105–208); lane 3, pGEX-SKAP55(204–299); lane 4, pGEX-SKAP55(300–369); lane 5, pGEX-SK1(204–238); lane 6, pGEX-SK2(239–255); lane 7, pGEX-SK3(256–276); lane 8, pGEX-SK4(277–298). The different truncated GST–SKAP55 fusion proteins were separated on a 10% SDS–polyacrylamide gel, transferred to nitrocellulose membranes and probed with Flag-tagged FYB SH3 protein and immunoblotted with anti-Flag monoclonal antibody. The sequence of the motifs contained within the GST fusion proteins is as follows: SK1, 204QISFLLKDLSSLTIPYEEDEEEEEKEETYDDIDGF238; SK2, 239DSPSCGSQCRPTILPGS255; SK3, 256VGIKEPTEEKEEEDIYEVLPD276; SK4, 277EEHDLEEDESGTRRKGDYASYY298. (Lower panel) FYB SH3 domain recognizes the SK4 region of SKAP55. The various GST–SH2 and –SH3 fusion proteins used in the far-western assay. Lane 1, pGEX-SK4; lane 2, CRKL SH3; lane 3, LCK SH3; lane 4, p85 SH3; lane 5, Src SH3; lane 6, ABL SH2; lane 7, GRB-2 N SH2; lane 8, FYN, SH2; lane 9, LCK SH2; lane 10, PLCγ SH2-N.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.