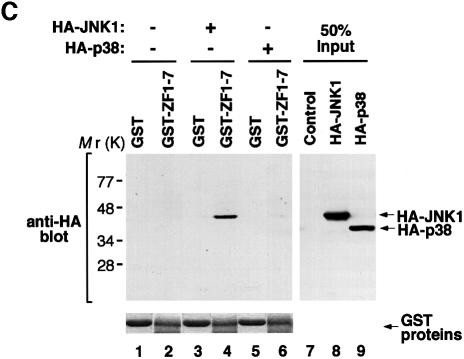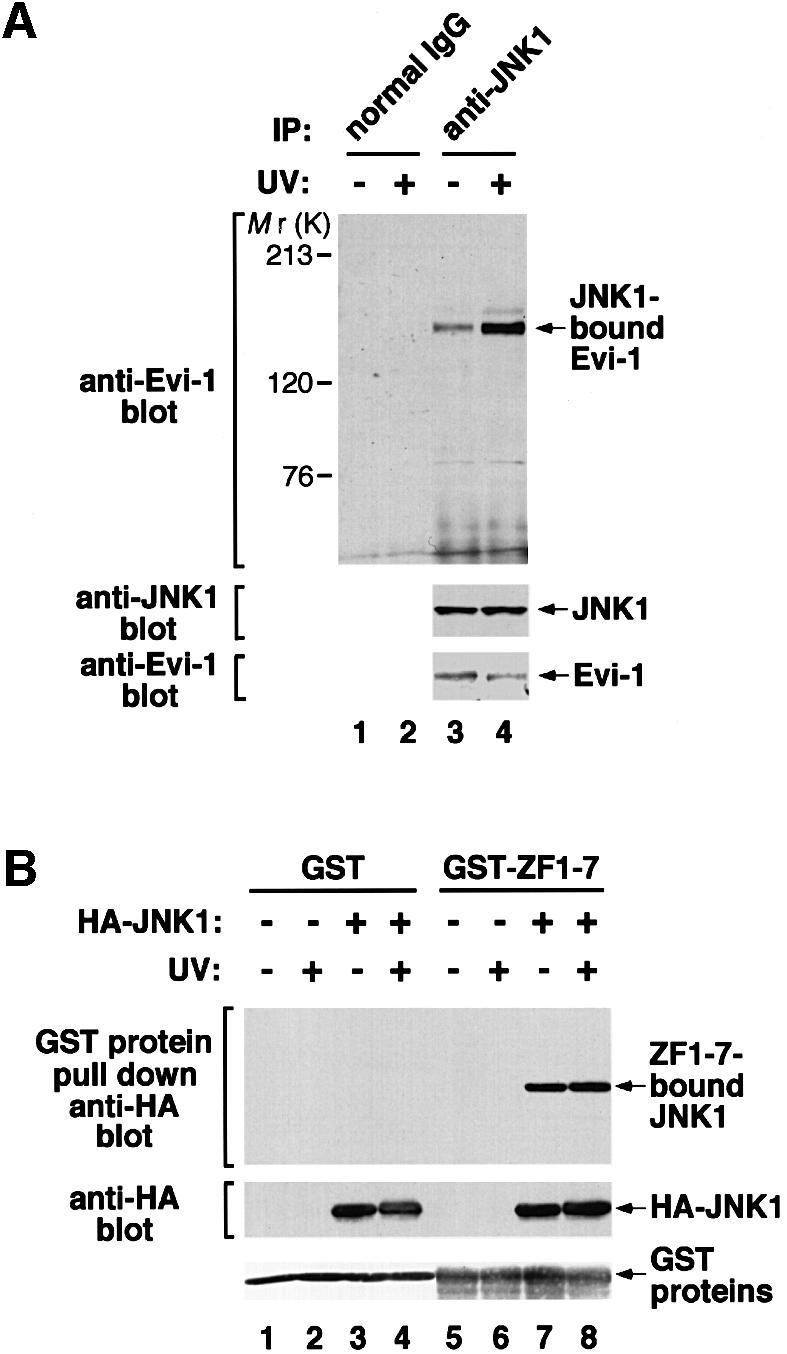
Fig. 5. (A) The constitutive interaction between Evi-1 and JNK1, and further stimulation by UV exposure. HEC1B cells were either left untreated or treated with 100 J/m2 UV. Whole-cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-JNK1, and bound Evi-1 was detected by immunoblotting with anti-Evi-1 (top). Expression of JNK1 and Evi-1 is monitored as indicated. (B) Evi-1 binds to both inactive and activated JNK. COS7 cells were transfected with HA-JNK1 and then either left untreated or treated with 60 J/m2 UV. Whole-cell extracts were incubated with GST or GST–ZF1–7, and bound JNK1 was detected by immunoblotting with 12CA5. HA-JNK1 and GST proteins were monitored as indicated. (C) JNK1, but not p38, binds to the first zinc finger domain of Evi-1. Whole-cell extracts from COS7 cells introduced with HA-JNK1 or HA-p38 were subjected to a pull-down assay using GST or GST–Evi-1(1–252) as indicated (top). Input of whole-cell extracts from HA-JNK1- or HA-p38-expressing COS7 cells is shown (lanes 8 and 9). GST fusion proteins are shown at the bottom.