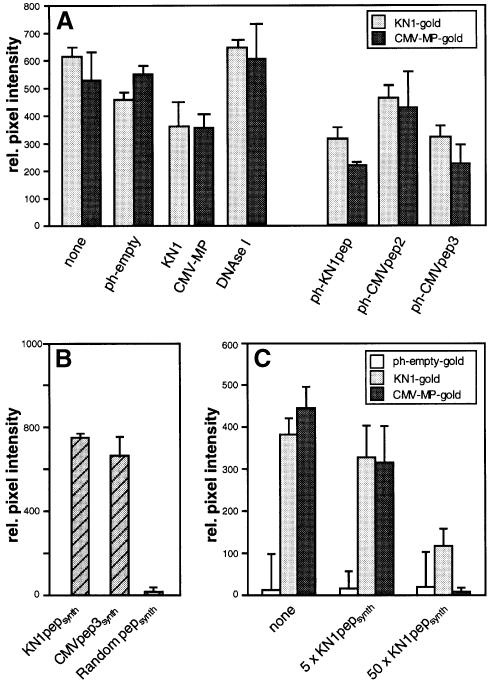
Fig. 3. Specificity of binding between isolated phage peptides and the tobacco W2 fraction proteins. (A) Competitive binding interactions between isolated tobacco W2 fraction proteins and KN1, CMV-MP and specific phage-displayed 12mer peptides. KN1 and CMV-MP were coated onto 6 nm gold particles and then used to determine specific protein interactions with the W2 cell fraction. Immobilized W2 fraction proteins (100 ng) were first incubated with the indicated probes (equimolar to the gold probe) and then subsequently competed with KN1-gold or CMV-MP-gold (0.2 µg). Note that experiments depicted on the left represent controls performed under the same conditions as described above for the phage peptide probes. (B) Ability of KN1pepsynth, CMVpep3synth and random pepsynth gold probes (0.2 µg) to bind immobilized W2 fraction proteins. (C) Competitive binding between KN1-gold, CMV-MP-gold or ph-empty-gold (all present at 0.2 µg) and a 5× or 50× molar excess of KN1pepsynth. Immobilized W2 fraction proteins were incubated with a mixture of competitor and gold probe. Interaction of protein-gold probes was visualized by silver enhancement. Data were compiled from three to four replicates for each experiment, and represent relative pixel densities (after subtraction of background as measured with BSA-gold); mean ± SEM.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.