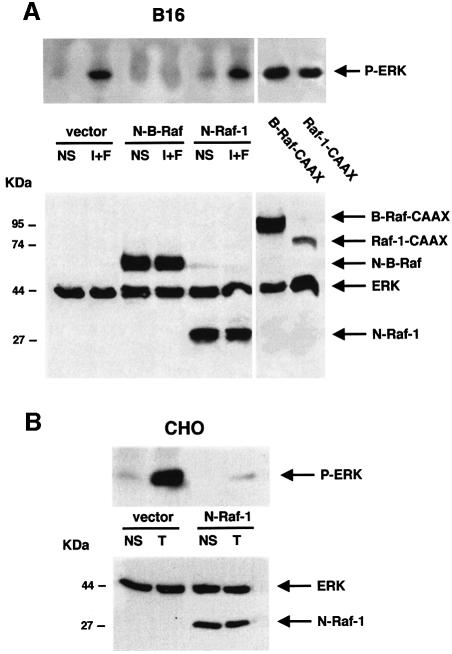
Fig. 2. In melanocytes, B-Raf mediates the cAMP-induced activation of ERK. (A) B16 cells were co-transfected with HA-tagged ERK1 together with an empty vector (vector), with dominant-negative mutants of B-Raf (N-B-Raf) or Raf-1 (N-Raf-1), or with constitutively active forms of B-Raf (B-Raf-CAAX) or Raf-1 (Raf-1-CAAX) tagged with the HA epitope. Cells were then treated or not (NS) for 10 min with the cAMP-elevating agents, IBMX plus forskolin (I+F). Lysates were then immunoprecipitated with an anti-HA antibody and subjected to western blot analysis using an anti-phopho ERK antibody (upper panel). A western blot of the same lysates was carried out using an anti-tag antibody (1/1000 dilution) as a control of the transfected protein expression (lower panel). (B) CHO cells co-transfected with HA–ERK1 and N-Raf-1 or an empty vector (vector), were left untreated (NS) or treated with TPA (T) for 10 min. HA–ERK activation was monitored as above (upper panel). A western blot of the cell lysates was performed using an anti-tag antibody as a control for transfected protein expression (lower panel).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.