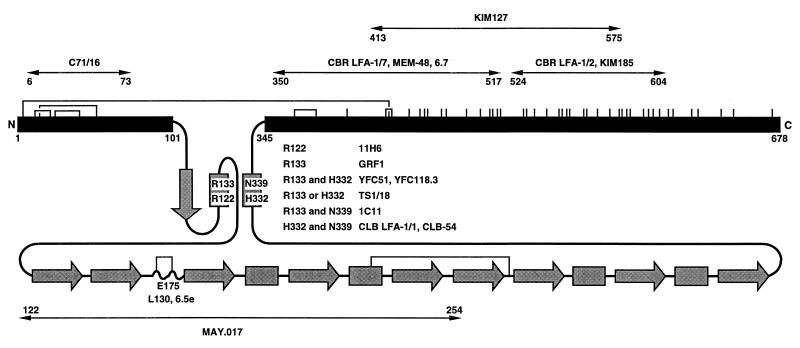
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the extracellular domain of the integrin β2 subunit. The conserved domain, from residues 102 to 344, is shaded gray and shown schematically according to its predicted secondary structure (C.H. and T.A.S., unpublished data). Arrows and rectangles represent predicted β-strands and α-helices, respectively. The regions from amino acids 1–101 and 345 to the end of the extracellular domain at 678 are shown as black bars and are to scale with one another but not with the conserved domain. All cysteines are shown as vertical lines, and the best characterized disulfides in β3 (39) are shown as connections between the homologues cysteines in β2. The localization of species-specific residues recognized by mAbs is described elsewhere (C.H. and T.A.S., unpublished data). Regions were mapped with mouse-human β2 chimeras and single amino acid substitutions. The regions defined by chimeras are further delimited by excluding regions at their borders identical between mouse and human, and thus regions specified in the figure are narrower than reported elsewhere.