Figure 4. Residues involved in agonist binding in the α1-ARs.
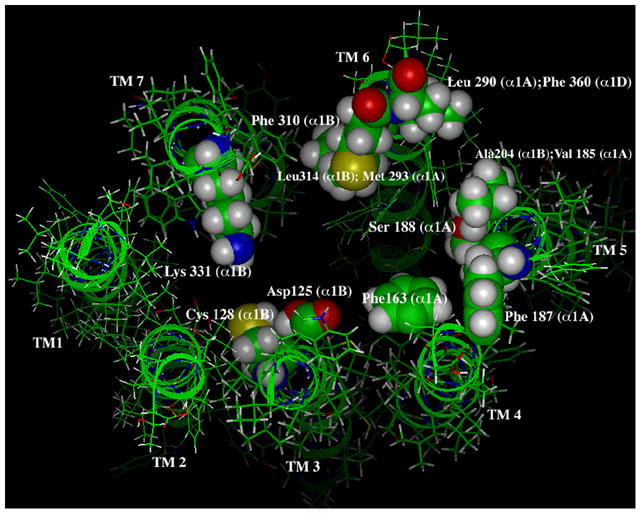
The view is looking down upon the extracellular face of the binding pocket. Mutagenesis studies have identified Asp 125 in TM 3 to interact with the protonated amine of catecholamines. Cys 128 in TM 3 is involved in agonist-selective signaling. Phe 163 in TM 4 is involved in aromatic interactions with the catechol ring as well as Phe 187 in TM 5. Ser 188 in TM 5 is involved in binding to the meta-hydroxyl of catecholamines. Ala 204 and Val 185 in TM 5 and Leu 314 and Met 293 in TM 6 are involved in conferring agonist selectivity between the α1-AR subtypes. Leu 290 and Phe 360 in TM 6 account for why the ability of the α1A-AR to accommodate bulky substituents in the para-position of catechol ring structures. Phe 310 in TM 6 interacts with the aromatic ring of catecholamines. Lys 331 in TM 7 is involved in α1-AR agonism by forming a salt-bridge to Asp 125 in TM 3. Numbering and residues are identified with their corresponding α1-AR subtypes in parentheses. Modeling was done independent of the rhodopsin structure and extracellular loops are removed for clarity.
