Figure 5. Residues involved in antagonist binding in the α1-ARs.
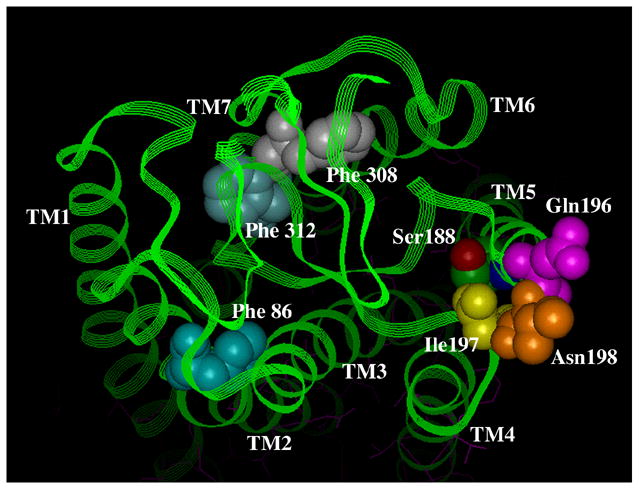
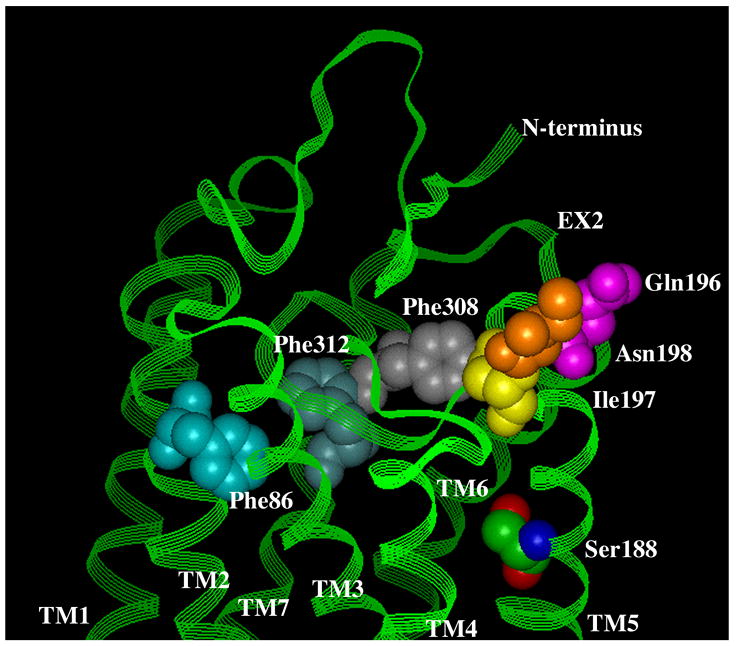
A. Surface view. B. Side view. Using the bovine rhodopsin α-carbon coordinates (64), residues involved in α1-AR antagonist binding were substituted in the corresponding positions of rhodopsin. Phe 86 in TM 2 discriminates the α1A-AR selective antagonist niguldipine as well as other dihydropyridine-type antagonists. Gln 196, Ile 197, and Asn 198, which are in the second extracellular loop, discriminate the α1A-AR selective antagonists phentolamine and WB4101. Phe 308 and Phe 312 in TM 7 are major aromatic contacts for most α1-AR antagonists as well as imidazoline-type agonists. Ser 188 in TM 5, which is involved in agonist binding, is shown for comparison of the depth of the antagonist-binding pocket. All residues are numbered according to the α1A-AR subtype.
