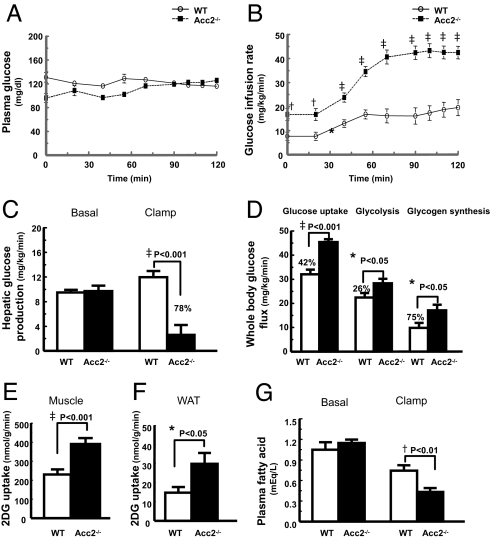
Fig. 2.
Knocking out of ACC2 significantly improved hepatic and peripheral insulin sensitivity in high-fat-fed mice. Peripheral and hepatic insulin sensitivity was assessed by means of hyperinsulinemic–euglycemic clamps. (A) Plasma glucose. (B) Glucose infusion rates. (C) Hepatic glucose production during hyperinsulinemic–euglycemic clamps. (D) Whole-body glucose uptake, whole-body glycolysis, and whole-body glycogen synthesis. (E) Skeletal muscle (gastrocnemius) glucose uptake. (F) Epididymal white adipose tissue (WAT) glucose uptake. (G) Suppression of plasma fatty acid concentrations during the clamps. The data are expressed as mean values ± SEM for nine mice per group. *, P < 0.05; †, P < 0.01; ‡, P < 0.001 (Acc2 −/− vs. WT); 2DG, 2-deoxy glucose.