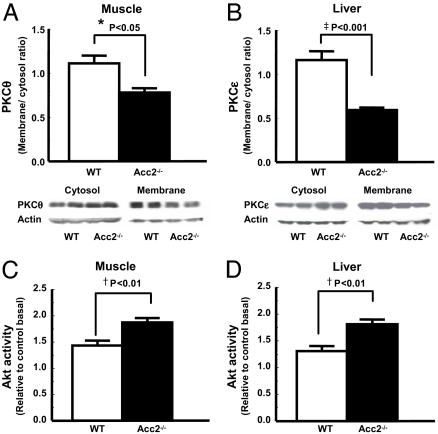
Fig. 3.
Knocking out of Acc2 increased Akt2 activity and decreased PKC membrane translocation. (C and D) Improved muscle and hepatic insulin sensitivity are associated with increased Akt2 activity in muscle (C) and liver (D). (A and B) Reduced membrane translocation of PKCθ in muscle (A) and PKCε in liver (B) may be directly involved in improving muscle and hepatic insulin signaling. Akt2 activity was assessed 14 min after i.p. insulin injection of 1 unit per kilogram of body weight. Data are expressed as mean values ± SEM for four to five mice per group. *, P < 0.05; †, P < 0.01; ‡, P < 0.001 (Acc2 −/− vs. WT).