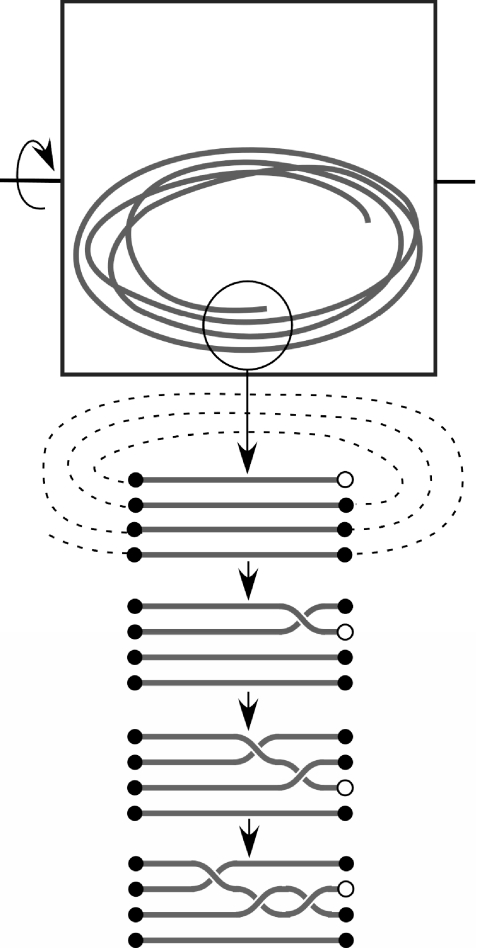
Fig. 6.
Schematic illustration of the simplified model for knot formation. Because of its stiffness, the string tends to coil in the box, as seen in Fig. 1, causing a number of parallel string segments to lie parallel adjacent the end segment. As discussed in the text, we model knots as forming due to a random series of braid moves of the end segment among the adjacent segments (diagrams at bottom). The overall connectivity of the segments is indicated by the dashed line.