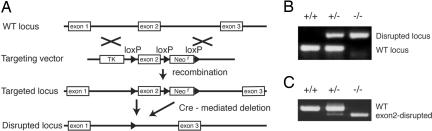
Fig. 1.
Generation of RAMP1−/− mice. (A) Schematic representation of the genomic structure of the relevant part of the RAMP1 WT allele; the targeting construct with PGK–TK and mouse PGK–Neor as negative and positive selectable markers, respectively; the allele after homologous recombination; and the disrupted RAMP1 allele after Cre-mediated deletion. (B) Genotyping of mouse tail DNA by using PCR analysis involving the primers described in Materials and Methods. The WT and mutant alleles have been shown as the 108- and 240-bp fragments, respectively. (C) RT-PCR analysis of RAMP1 transcripts obtained from the thymus. Total RNA isolated from the thymus was reverse transcribed and amplified by using RAMP1-specific primer pairs.