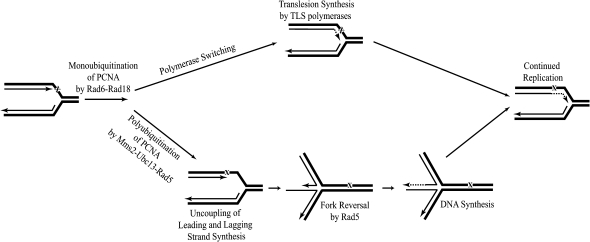
Figure 4.
Model for the Role of Rad5 in Lesion Bypass by Template Switching
If replication stalls at a DNA lesion, the PCNA monoubiquitination by Rad6-Rad18 enables polymerase switch and lesion bypass by the TLS polymerases to occur. Alternatively, polyubiquitination of PCNA by Mms2-Ubc13-Rad5 promotes PRR. In this model, when replication on the leading strand is blocked by a DNA lesion, lagging strand synthesis continues on. Rad5 then gains access to the asymmetric forks and unwinds both the lagging and leading nascent DNA strands, followed by annealing them as well as annealing the template strands. By this fork regression activity a four-way junction intermediate called “chicken foot” is formed. Following that, a DNA polymerase extends the 3′ OH end of the leading nascent strand by copying from the nascent lagging strand. Finally, the back-migration of the four way junction completes error-free replication through the DNA damage.