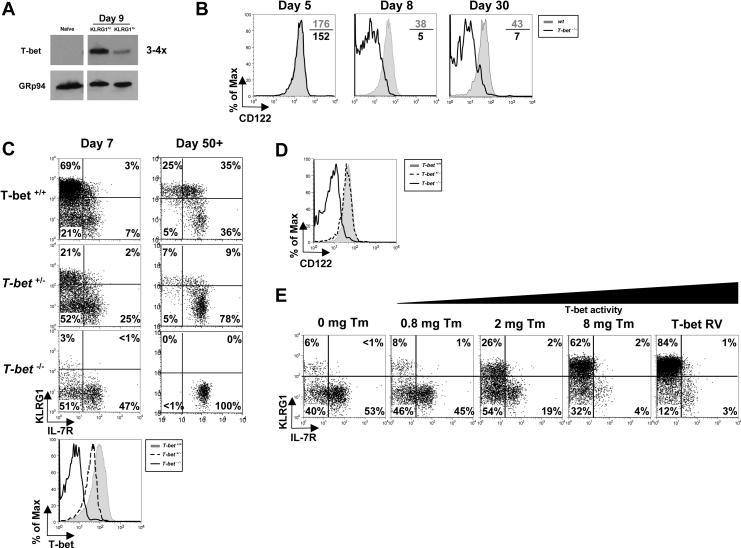
Figure 6.
T-bet functions in both MPECs and SLECs according to an expression gradient.
(A) Naïve and day 8 KLRG1hi IL-7Rlo SLECs or KLRG1lo IL-7Rhi MPECs were sorted and examined by Western blotting T-bet and GRp94 levels.
(B) wt and T-bet−/− P14 CD8 T cells were analyzed 5, 8 and 30 days pi for CD122 expression.
(C) T-bet+/+, T-bet+/− or T-bet−/− P14 CD8 T cells were analyzed 7 and 30 days pi for KLRG1 and IL-7R expression and T-bet expression (bottom histogram plot).
(D) T-bet+/+, T-bet+/− or T-bet−/− P14 memory CD8 T cells were analyzed 30 days pi for CD122 expression
(E) T-bet−/− P14 CD8 T cells were transduced with T-bet RV or one expressing T-bet fused to the estrogen receptor (T-bet:ER) and transferred into mice subsequently infected with LCMV. Mice were treated with 0 – 8 mg of Tamoxifen (Tm) during infection and on day 7 pi, GFP+ donor splenocytes were analyzed for expression of KLRG1 and IL-7R.