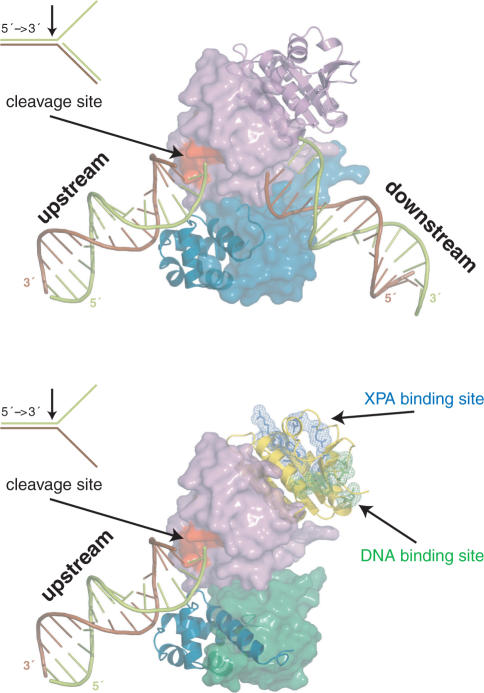
Figure 6.
Models for the function of the archaeal homodimeric XPF (top) and human ERCC1/XPF heterodimer (bottom) constructed from the structure of the XPF homodimer bound to dsDNA (2bgw), the free structure of ERCC1/XPF C-terminal interacting domains (1z00) and the current structure of the ERCC1 central domain (2jpd). For the homodimer, one protomer is shown in a cartoon and the other in a surface representation. Accordingly, for the heterodimer ERCC1 is in a cartoon and XPF in a surface representation. The protein domains in both cases are colored as in Figure 1A.