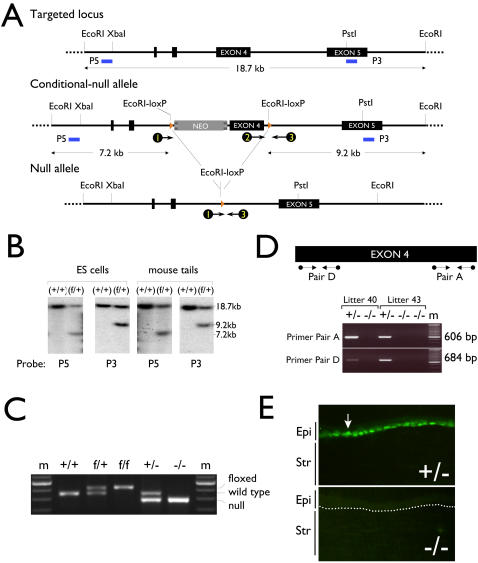
Figure 1. Generation of basonuclin-null mouse.
A, A graphic depiction of the knockout strategy. The targeted locus (∼18.7 kb) of the basonuclin gene is shown at the top. Restriction sites relevant to cloning and detection of the conditional allele are indicated. Exons are depicted as black boxes and the Southern probes (P5 and P3) are indicated as short blue lines. Shown below the targeted locus is the structure of basonuclin conditional-null allele, which consists of a neo gene upstream from the Exon 4. The neo gene and the Exon 4 are flanked by loxP sites. To facilitate the detection of the conditional-null allele, two new Eco RI sites are generated with the insertion of the lox P sites. Upon Eco RI digestion, the wild type allele produces a single 18.7 kb fragment, whereas that of the conditional-null allele, two fragments of sizes 7.2 kb (detected by 5′ probe) and 9.2 kb (3′ probe). The null-allele, which is generated after the excision of the neo and the Exon 4 by Cre recombinase, is shown below the conditional-null allele. PCR primers, depicted as circle-ended arrows, are designed to facilitate genotyping. B, Successful homologous recombination of the targeting vector was verified by Southern blots. Genomic DNAs from ES cells and founder mice tails were digested with Eco RI and analyzed by Southern blot using 5′ (P5) and 3′ (P3) probes (A, blue lines) outside the targeted region (defined by the lox P sites). The genotypes are indicated at the top of the Southern image, molecular weight markers are shown to the right and the probes at the bottom. f, the allele with inserted loxP. C, The null allele was generated by mating the female conditional knockout mice with ZP3-Cre males to create a Bnc1 (flox/+);ZP3-Cre female, which was then crossed with normal males. The genotypes of Bnc1 (+/+) (f/+), (f/f), (+/−), and (−/−) mice were identified by PCR and the deletion of Exon 4 was verified by PCR with primers indicated in A. In the PCR, all three primers were present, primers 2 and 3 detected the wild type and conditional alleles and primers 1 and 3 detected the null allele. The primer extension step was limited so that primers 1 and 3 could not produce a fragment with the wild type and the conditional allele. floxed, loxP-inserted. D, The absence of basonuclin mRNA was demonstrated with two pairs (A and D) of PCR primers targeting different regions of the Exon 4 (top panel). Tail RNAs of three Bnc1 (−/−) mice from two litters were assayed. The litters and genotypes are indicated at the top of the gel image and molecular weight of the amplicon on the right. E, The absence of basonuclin protein was demonstrated by immunostaining. The arrow shows an example of a basonuclin-positive cell. A dotted line indicates the position of basement membrane. Epi, epithelium; Str, stroma.