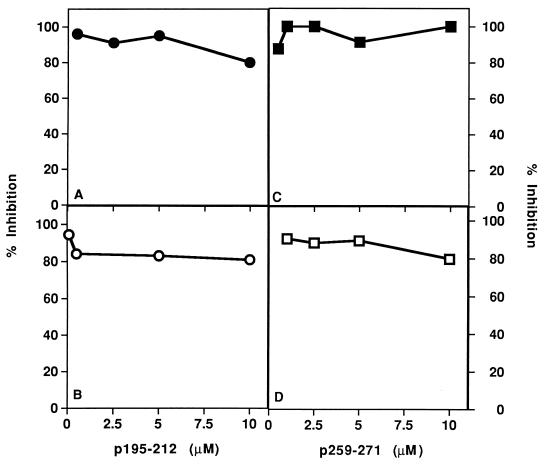
Figure 4.
Inhibition of the in vivo priming by oral administration of a dual analog. SJL mice (A and B) and BALB/c mice (C and D) were injected intradermally in the hindfoot pads with 10 μg of p195-212 and 20 μg p259-271, respectively, in CFA. Analog Lys-262–Ala-207 (500 μg in 300 μl of PBS) was administered per os either concomitant with (A, •, and C, ▪) or a week after (B, ○, and D, □) the priming. LN cells obtained from mice 10 days following immunization were incubated in the presence of various concentrations of p195-212 or p259-271 for 96 hr. Thereafter, [3H]thymidine was added and 16 hr later cells were harvested and radioactivity was counted. Results are expressed as percent of inhibition of the specific proliferative responses to the myasthenogenic peptide, as measured in LN cells of mice that were primed but not inhibited (for SJL, 71 cpm background, 5,826 cpm at optimal peptide concentration; for BALB/c, 246 cpm background, 6,904 cpm at optimal peptide concentration).