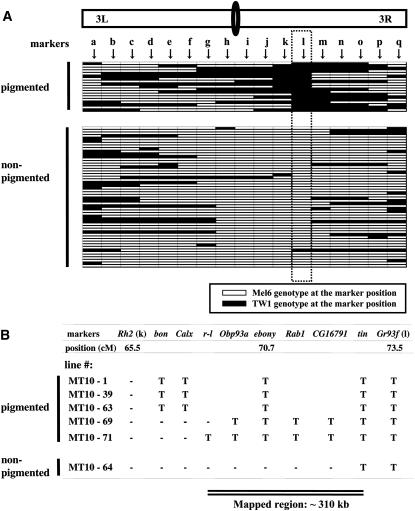
Figure 2.—
Genetic mapping of the thoracic trident pigmentation phenotype using 73 homozygous recombinant lines constructed between TW1 and Mel6. (A) Genotypes of the pigmented (n = 19) and nonpigmented (n = 54) phenotype lines at 17 restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) markers (a–q) on the third chromosome: a, Gr61d; b, gry; c, Gr64A; d, lama; e, Gr65c; f, Dhpr; g, Gr68d; h, Or74a; i, desat2; j, pnr; k, Rh2; l, Gr93f; m, RpS3; n, ssh; o, Pr; p, Gr98a; q, Ptx. Horizontal bars indicate genotypes of the recombinant lines. The dotted square indicates the genotypes at Gr93f marker that had almost complete association with the phenotype (r2 = 0.93). Note that one exceptional line that showed nonpigmented phenotype but had TW1 genotype at Gr93f is represented as MT10-64 in B. RFLP markers were developed by direct sequencing PCR fragments of ∼600–900 bp from Mel6 and TW1. Further information on RFLP markers can be provided upon request. Primers were designed by Primer3 software (Rozen and Skaletsky 2000) from the publicly available genome sequence (Adams et al. 2000). DNA was extracted from one male each from Mel6 and TW1 using the GeneElute Mammalian Genomic DNA kit (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis). PCR products were obtained from these genomic samples by the AmpliTaq Gold PCR kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) and were purified using MultiScreen-FB filter plates (Millipore, Billerica, MA). These purified products were directly sequenced on both strands using the BigDye terminator cycle sequencing kit version 3 (Applied Biosystems). The third chromosome recombinant lines were constructed from F2 backcrossed individuals in the Mel6 homozygous background. The line was backcrossed twice (including the F2 backcross) to Mel6 and had two generations of recombination opportunity. The lines were made homozygous using balancers in the last step. Note that these third chromosome recombinants possess the X and the second chromosomes from Mel6. (B) Genotypes at eight additional RFLP markers in six recombinant lines from A that had their breakpoints between markers Rh2 (k) and Gr93f (l). T indicates TW1 genotype and “-” indicates Mel6 genotype. Two critical lines, MT10-69 and MT10-64, indicate that the ∼310-kb region between markers r-l and tin is responsible for the phenotype.