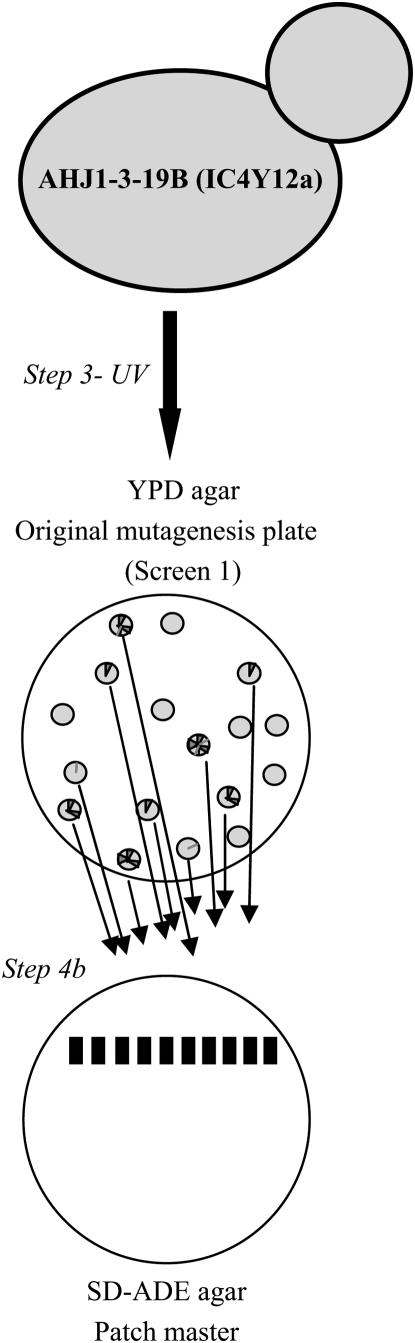
Figure 1.—
Overview of course research project to isolate and characterize yeast mutants with defects in mitotic chromosome segregation. The research project was conducted in seven steps. (1) Yeast strains were tested for correct genotype/phenotype. (2) The YAC loss rate in the wild-type unmutagenized yeast strain was determined. (3) The YAC-containing yeast strain was mutagenized with UV light. (4) Mutants with increased YAC loss were identified by a series of three screens: (a) screen 1, in which mutagenized colonies were visually screened for increased sectoring phenotype; (b) screen 2, in which an SD–ADE patch master was made using the white portion of a sectored colony from screen 1, the resulting SD–ADE patches were single-colony purified on YPD, and the sectoring phenotype was observed; and (c) screen 3, in which a fresh SD–ADE patch master was made using the white portion of a sectored colony from the YPD plate in screen 2, the resulting SD–ADE patches were single-colony purified on YPD, and the sectoring phenotype was observed. (5) Mutants were analyzed genetically for mode of inheritance (i.e., dominant, recessive), complementation analysis, and temperature sensitivity. (6) YAC loss rate was determined in the mutants. (7) Independent experiments were designed and conducted.