Figure 2.
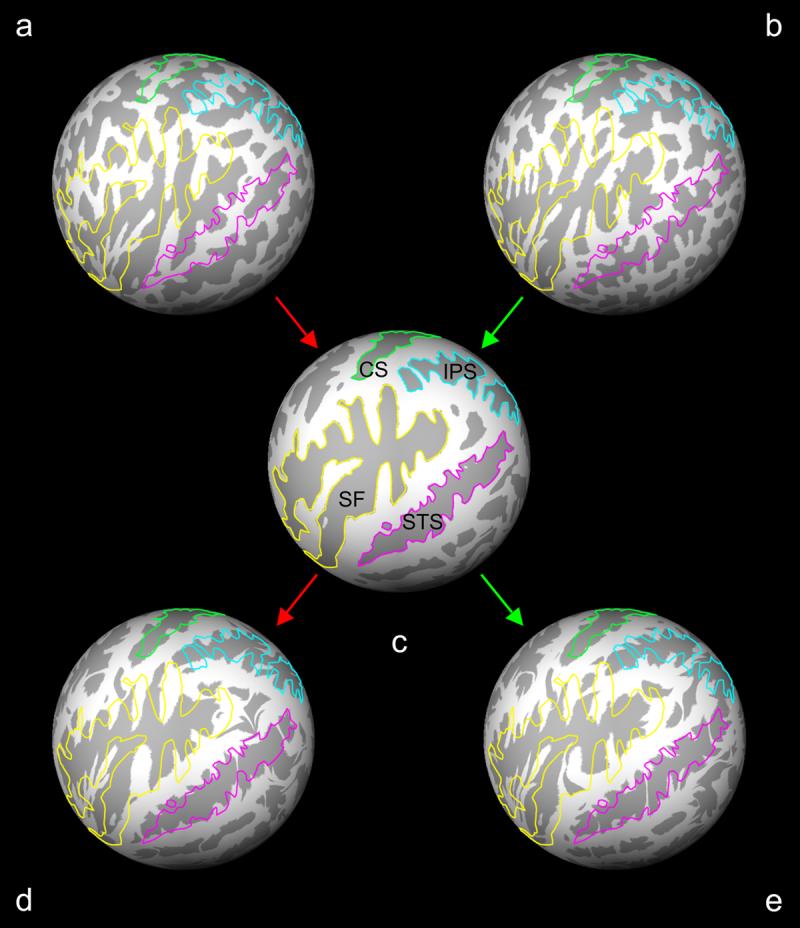
Spherical registration and metric distortion. Spheres (a, d) and (b, e) are reconstructed brain surfaces from a control subject and a schizophrenia patient, respectively. A subject sphere was registered to the average subject template sphere (c) using a non-linear warping algorithm. The metric distortion required to correctly align gyri (light gray) and sulci (dark gray) was a direct reflection of the cortical folding distortions and convolutions between a subject sphere and the template average. Outlines of the central sulcus (CS, light green), intraparietal sulcus (IPS, light blue), Sylvian fissure (SF, yellow) and superior temporal sulcus (STS, magenta) based on the average subject template sphere (c) are overlaid on the subject spheres before and after registration to illustrate the process.
