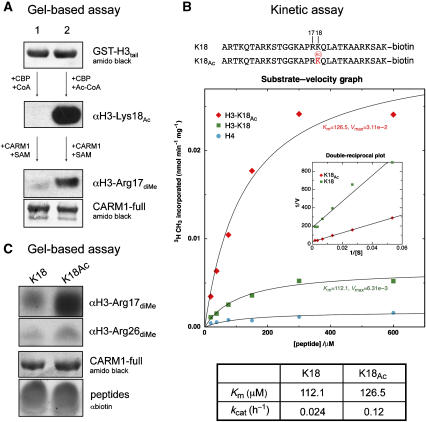
Figure 5.
Crosstalk between histone modifications. (A) Lysine pre-acetylation of H3 N-terminal tail potentiates CARM1 methylation in vitro. Equal amounts of GST-H3tail are subjected to either a mock acetylation followed by CARM1-full methylation (lane 1), or CBP acetylation followed by CARM1-full methylation (lane 2). Before CARM1 methylation, GST-H3tail was purified by Glutathione Sepharose to remove CBP and residual CoA/Ac-CoA. Acetylation and methylation are probed by anti-acetyl-Lys18 and anti-dimethyl-Arg17 antibodies, respectively. (B) Top panel: sequences of the H3 peptides used in the kinetic assay. Middle panel: CARM1-full was incubated with K18-peptide (green box), K18Ac-peptide (red diamond) or histone H4-peptide (negative control, cyan circle). Product formation was plotted versus substrate concentration (0.031, 0.063, 0.125, 0.25, 0.5 and 1 mM) and nonlinear regression was performed for determination of Km and kcat values. Inset: Lineweaver–Burk plot of 1/V versus 1/[S]. Bottom panel: table of Km and kcat values. (C) Gel-based methylation assay for K18-peptide and K18Ac-peptide, detected by anti-dimethyl-Arg17 or anti-dimethyl-Arg26 antibodies. Loading controls for CARM1-full and H3 peptides are shown.