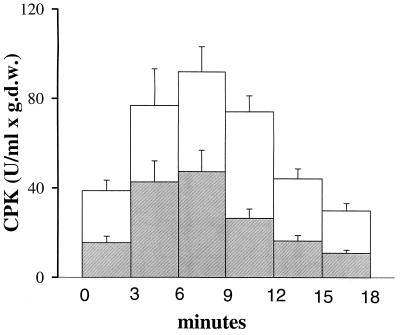
Figure 2.
Chronic exposure to ethanol reduces CK release during postischemic reperfusion. CK (units/ml per heart gram-dry-weight) was measured in the coronary effluent during 3-min intervals of postischemic reperfusion from hearts isolated from ethanol-treated guinea pigs as described in Fig. 1 (shaded bars) and controls (open bars). Release of creatine was significantly less from hearts of ethanol-treated animals compared with controls during all 3-min collection periods (P < 0.05). Adenosine A1 receptor blockade by DPCPX completely abolished the protective effect of ethanol consumption on myocyte injury. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.