Abstract
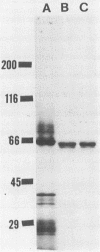
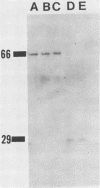
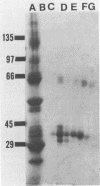
Two proteins from parasporal crystals of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis were purified to electrophoretic homogeneity by gel filtration and anion-exchange chromatography. The larger of the two proteins (molecular weight, 68,000) was not cytolytic, whereas the smaller protein (molecular weight, 28,000) was highly cytolytic when assayed against rat erythrocytes. When these proteins were assayed against larvae of the yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti, the larger protein was at least 100-fold more toxic than the smaller protein. Although proteolytic activity was not detected in solubilized crystals nor in purified protein preparations, the toxin (molecular weight, 68,000) was readily degraded to smaller, nontoxic molecules, even when maintained at 4 degrees C. Mixtures of the two purified proteins were significantly more toxic to mosquito larvae than was either protein alone. Thus, it is likely that both the mosquitocidal and the cytolytic protein play roles in the overall insecticidal action of the parasporal crystal produced by this bacterium.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews R. E., Jr, Bibilos M. M., Bulla L. A., Jr Protease activation of the entomocidal protoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):737–742. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.737-742.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ang B. J., Nickerson K. W. Purification of the protein crystal from Bacillus thuringiensis by zonal gradient centrifugation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Oct;36(4):625–626. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.4.625-626.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. L., Rohrmann G. F., Beaudreau G. S. Delta endotoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):39–46. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.39-46.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulla L. A., Jr, Davidson L. I., Kramer K. J., Jones B. L. Purification of the insecticidal toxin from the parasporal crystal of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Dec 14;91(3):1123–1130. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91997-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dadd R. H. Alkalinity within the midgut of mosquito larvae with alkaline-active digestive enzymes. J Insect Physiol. 1975 Nov;21(11):1847–1853. doi: 10.1016/0022-1910(75)90252-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. M., Lee S. G., Andrews R. E., Jr, Klowden M. J., Bulla L. A., Jr Separation of the cytolytic and mosquitocidal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 31;126(2):961–965. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90279-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibarra J. E., Federici B. A. Isolation of a relatively nontoxic 65-kilodalton protein inclusion from the parasporal body of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):527–533. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.527-533.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insell J. P., Fitz-James P. C. Composition and Toxicity of the Inclusion of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jul;50(1):56–62. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.1.56-62.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klowden M. J., Bulla L. A., Jr Oral toxicity of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis to adult mosquitoes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Sep;48(3):665–667. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.3.665-667.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klowden M. J., Bulla L. A., Jr, Stoltz R. L. Susceptibility of larval and adult Simulium vittatum (Diptera: Simuliidae) to the solubilized parasporal crystal of Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis. J Med Entomol. 1985 Jul 26;22(4):466–467. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/22.4.466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klowden M. J., Held G. A., Bulla L. A., Jr Toxicity of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis to adult Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Aug;46(2):312–315. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.2.312-315.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. G., Eckblad W., Bulla L. A., Jr Diversity of protein inclusion bodies and identification of mosquitocidal protein in Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 31;126(2):953–960. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90278-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margalit J., Dean D. The story of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis (B.t.i.). J Am Mosq Control Assoc. 1985 Mar;1(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfannenstiel M. A., Couche G. A., Ross E. J., Nickerson K. W. Immunological relationships among proteins making up the Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis crystalline toxin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):644–649. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.644-649.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe E. S., Nickerson K. W., Bulla L. A., Jr, Aronson J. N. Separation of spores and parasporal crystals of Bacillus thuringiensis in gradients of certain x-ray contrasting agents. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Dec;30(6):1052–1053. doi: 10.1128/am.30.6.1052-1053.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temeyer K. B. Larvicidal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis in the dipteran Haematobia irritans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 May;47(5):952–955. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.5.952-955.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W. E., Ellar D. J. Bacillus thuringiensis var israelensis crystal delta-endotoxin: effects on insect and mammalian cells in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Sci. 1983 Mar;60:181–197. doi: 10.1242/jcs.60.1.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrell D. J., Bulla L. A., Jr, Andrews R. E., Jr, Kramer K. J., Davidson L. I., Nordin P. Comparative biochemistry of entomocidal parasporal crystals of selected Bacillus thuringiensis strains. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1052–1062. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1052-1062.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrell D. J., Davidson L. I., Bulla L. A., Jr, Ramoska W. A. Toxicity of parasporal crystals of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis to mosquitoes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Oct;38(4):656–658. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.4.656-658.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilton B. E., Klowden M. J. Solubilized crystal of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis: effect on adult house flies, stable flies (Diptera: Muscidae), and green lacewings (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). J Am Mosq Control Assoc. 1985 Mar;1(1):97–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yousten A. A., Rogoff M. H. Metabolism of Bacillus thuringiensis in relation to spore and crystal formation. J Bacteriol. 1969 Dec;100(3):1229–1236. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.3.1229-1236.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]