Figure 6. The antiviral efficacy of PNAPBS- and PNAA-loop-MTD peptide conjugates.
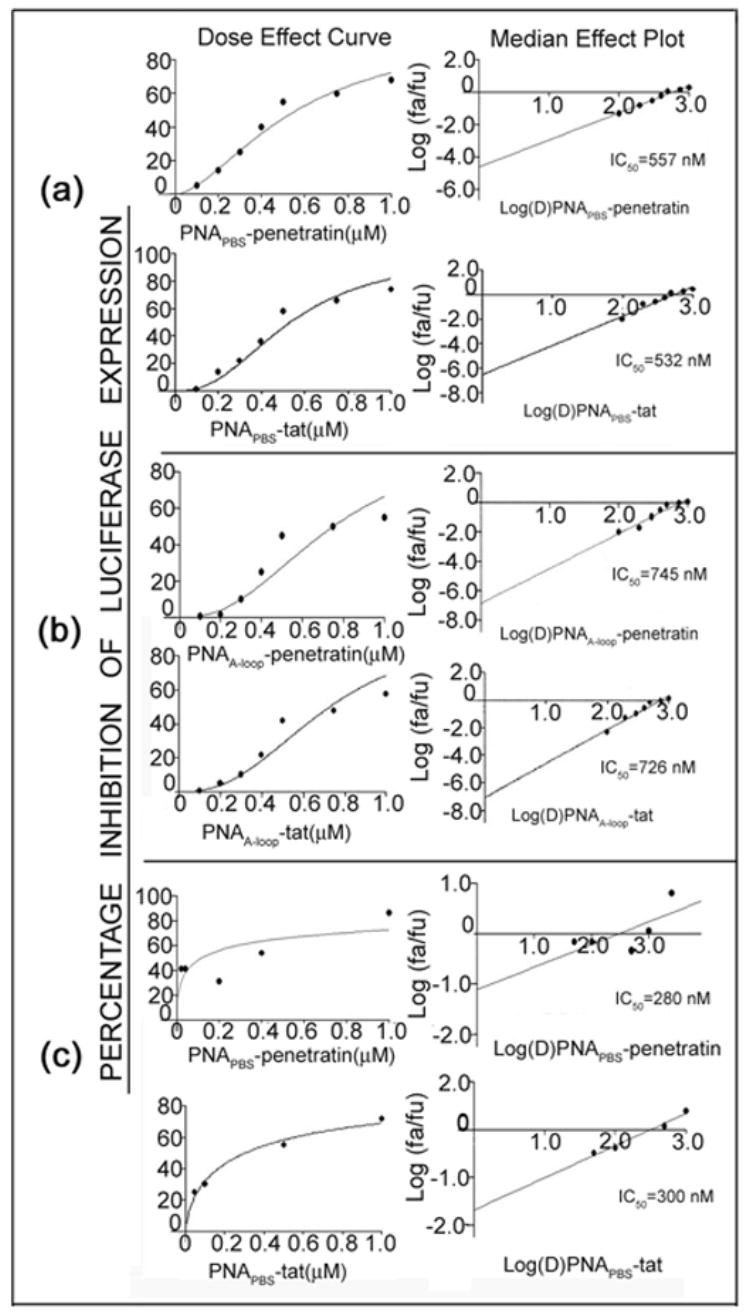
T lymphocyte cells were first infected with pseudo-HIV-1 virions for 2 h in the presence of varying concentrations of either PNAPBS-MTD peptide conjugates (a) or PNAA-loop-MTD conjugates (b). Unconjugated PNA and peptides alone were included as control. The infected cells were further grown in the presence of increasing amounts of respective PNA-MTD conjugates for 48 h. The cells were harvested, washed, and lysed. An aliquot of the cell lysate was examined for luciferase activity and the percentage of inhibition of luciferase expression in treated cells was determined with respect to that in untreated control. Median-effect plots and dose-effect curves were calculated. The dose median values (IC50) for individual PNAPBS- and PNAA-Loop-MTD peptide conjugates are indicated. Antiviral efficacy was also examined in PHA stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear lymphocyte (PBMC) cells using PNAPBS-peptides (c) and the infected cells were grown for seven days before harvesting. The cell lysate was examined for luciferase activity as described above. Naked PNA and peptide alone had no effect on antiviral efficacy as naked PNA are found to be incompetent of cellular uptake and presence of peptide had no effect on viral infectivity. In both these cases the levels of luciferase expression was found to be similar to the untreated virions, therefore no values can be generated to put in the CalcuSyn software.
