Figure 2.
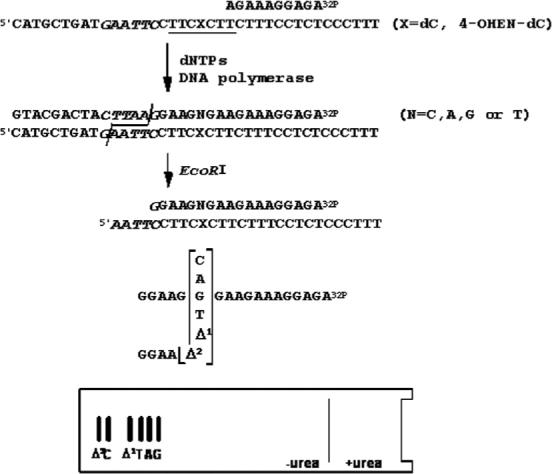
Diagram of the method used to determine miscoding specificity. Unmodified or 4-OHEN-dC-modified 38-mer templates were annealed to a 32P-labeled 10-mer primer. Primer extension reactions catalyzed by Y-family enzymes (pol η, κΔC or ι) were conducted in the presence of four dNTPs. Fully extended products formed during DNA synthesis were recovered from the polyacrylamide gel, annealed with a complementary 38-mer, cleaved with EcoRI, and subjected to two-phase PAGE as described in Materials and Methods. To determine miscoding specificity, the mobility of the reaction products was compared with those of 18-mer standards containing dC, dA, dG, or dT opposite the lesion and one base (Δ1) or two-base (Δ2) deletions.
