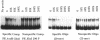Abstract
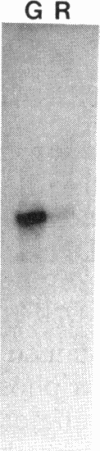
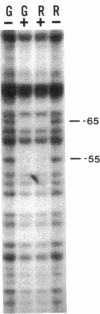
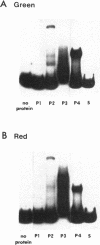
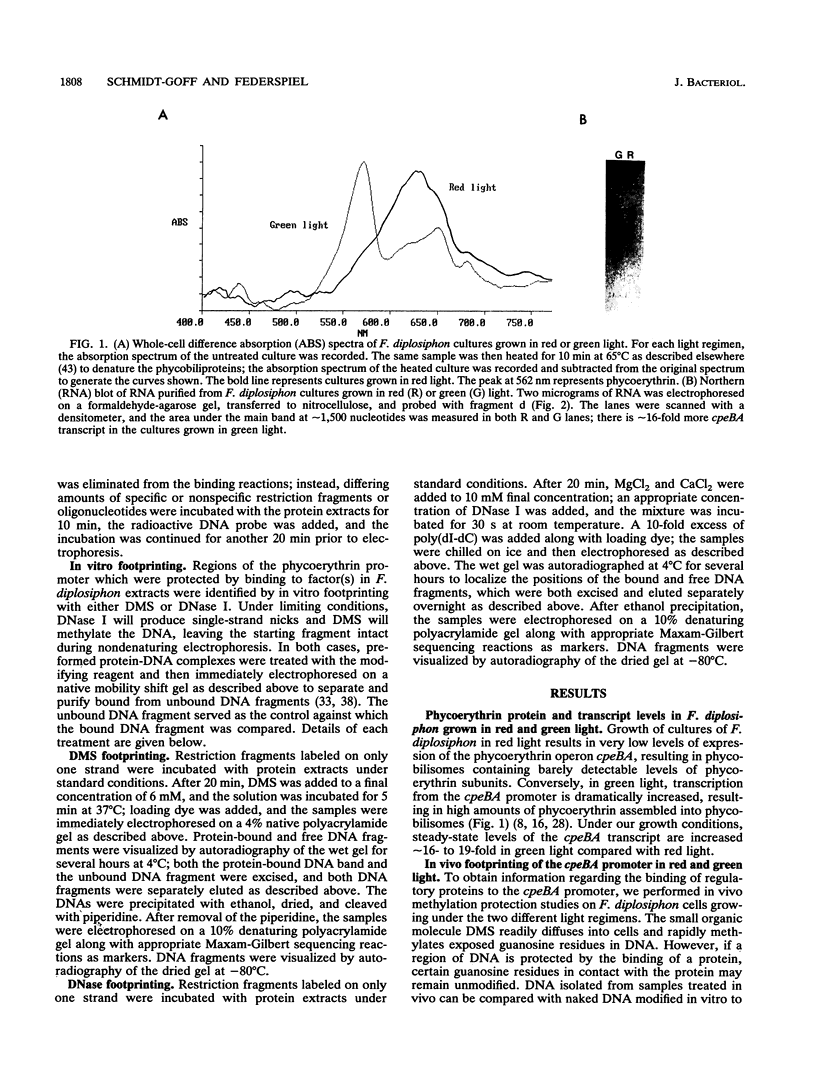
Certain filamentous cyanobacteria, such as Fremyella diplosiphon, modulate the components of their light-harvesting complexes, the phycobilisomes, and undergo complex morphological changes in response to the wavelength of incident light, or light quality. The operon encoding the subunits of phycoerythrin, cpeBA, is transcriptionally activated in green light and is expressed at very low levels in red light. To begin elucidating the signal transduction pathway between the detection of specific light wavelengths and changes in gene expression, we have used in vivo footprinting to show that a protein is bound to the region upstream of the cpeBA transcription start site in both red and green light: two guanosine residues at -55 and -65 bp are protected from dimethyl sulfate modification in vivo. Using DNA mobility shift gel electrophoresis, we have shown that partially purified extracts of F. diplosiphon from both red and green light contain DNA-binding activity specific for the cpeBA promoter region. Using in vitro footprinting with dimethyl sulfate and DNase I, we have defined a binding site for this putative transcription factor, designated PepB (phycoerythrin promoter-binding protein), that extends from -67 to -45 bp on the upper strand and from -62 to -45 bp on the bottom strand, relative to the transcription start site. The binding site includes two hexameric direct repeats separated by 4 bp, TTGTTAN4TTGTTA. We conclude from these results that PepB is bound to the region upstream of the cpeBA promoter in F. diplosiphon in both red and green light. Therefore, additional factors or protein modifications must be required to allow light-regulated transcription of this operon.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albright L. M., Huala E., Ausubel F. M. Prokaryotic signal transduction mediated by sensor and regulator protein pairs. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:311–336. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustos S. A., Golden S. S. Expression of the psbDII gene in Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942 requires sequences downstream of the transcription start site. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7525–7533. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7525-7533.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley P. B., Lemaux P. G., Grossman A. Molecular characterization and evolution of sequences encoding light-harvesting components in the chromatically adapting cyanobacterium Fremyella diplosiphon. J Mol Biol. 1988 Feb 5;199(3):447–465. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90617-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Cashmore A. R. Binding of a pea nuclear protein to promoters of certain photoregulated genes is modulated by phosphorylation. Plant Cell. 1989 Nov;1(11):1069–1077. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.11.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federspiel N. A., Grossman A. R. Characterization of the light-regulated operon encoding the phycoerythrin-associated linker proteins from the cyanobacterium Fremyella diplosiphon. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):4072–4081. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.4072-4081.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federspiel N. A., Scott L. Characterization of a light-regulated gene encoding a new phycoerythrin-associated linker protein from the cyanobacterium Fremyella diplosiphon. J Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;174(18):5994–5998. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.18.5994-5998.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin P. M., Sarokin L., Memelink J., Chua N. H. Molecular light switches for plant genes. Plant Cell. 1990 May;2(5):369–378. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.5.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannoni S. J., Turner S., Olsen G. J., Barns S., Lane D. J., Pace N. R. Evolutionary relationships among cyanobacteria and green chloroplasts. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3584–3592. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3584-3592.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer A. N. Light harvesting by phycobilisomes. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1985;14:47–77. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.14.060185.000403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer A. N. Phycobilisomes: structure and dynamics. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:173–198. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.001133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. S., Mahoney M. E., Wulff D. L., Rosenberg M. Identification of the DNA binding domain of the phage lambda cII transcriptional activator and the direct correlation of cII protein stability with its oligomeric forms. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):184–195. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. S., Pfarr D., Strickler J., Rosenberg M. Characterization of the transcription activator protein C1 of bacteriophage P22. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14388–14397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. S., Wulff D. L., Rosenberg M. Bacteriophage lambda protein cII binds promoters on the opposite face of the DNA helix from RNA polymerase. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):703–708. doi: 10.1038/304703a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houmard J., Capuano V., Colombano M. V., Coursin T., Tandeau de Marsac N. Molecular characterization of the terminal energy acceptor of cyanobacterial phycobilisomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2152–2156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houmard J., Capuano V., Coursin T., Tandeau de Marsac N. Genes encoding core components of the phycobilisome in the cyanobacterium Calothrix sp. strain PCC 7601: occurrence of a multigene family. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5512–5521. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5512-5521.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomax T. L., Conley P. B., Schilling J., Grossman A. R. Isolation and characterization of light-regulated phycobilisome linker polypeptide genes and their transcription as a polycistronic mRNA. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2675–2684. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2675-2684.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda S., Mizuno T. Evidence for multiple OmpR-binding sites in the upstream activation sequence of the ompC promoter in Escherichia coli: a single OmpR-binding site is capable of activating the promoter. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):501–503. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.501-503.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino K., Shinagawa H., Amemura M., Kimura S., Nakata A., Ishihama A. Regulation of the phosphate regulon of Escherichia coli. Activation of pstS transcription by PhoB protein in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 5;203(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazel D., Guglielmi G., Houmard J., Sidler W., Bryant D. A., Tandeau de Marsac N. Green light induces transcription of the phycoerythrin operon in the cyanobacterium Calothrix 7601. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8279–8290. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Taylor R. K., Mekalanos J. J. Cholera toxin transcriptional activator toxR is a transmembrane DNA binding protein. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oelmüller R., Conley P. B., Federspiel N., Briggs W. R., Grossman A. R. Changes in Accumulation and Synthesis of Transcripts Encoding Phycobilisome Components during Acclimation of Fremyella diplosiphon to Different Light Qualities. Plant Physiol. 1988 Dec;88(4):1077–1083. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.4.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oelmüller R., Grossman A. R., Briggs W. R. Photoreversibility of the Effect of Red and Green Light Pulses on the Accumulation in Darkness of mRNAs Coding for Phycocyanin and Phycoerythrin in Fremyella diplosiphon. Plant Physiol. 1988 Dec;88(4):1084–1091. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.4.1084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oelmüller R., Grossman A. R., Briggs W. R. Role of Protein Synthesis in Regulation of Phycobiliprotein mRNA Abundance by Light Quality in Fremyella diplosiphon. Plant Physiol. 1989 Aug;90(4):1486–1491. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.4.1486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popham D. L., Szeto D., Keener J., Kustu S. Function of a bacterial activator protein that binds to transcriptional enhancers. Science. 1989 Feb 3;243(4891):629–635. doi: 10.1126/science.2563595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarokin L. P., Chua N. H. Binding sites for two novel phosphoproteins, 3AF5 and 3AF3, are required for rbcS-3A expression. Plant Cell. 1992 Apr;4(4):473–483. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.4.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasse-Dwight S., Gralla J. D. Footprinting protein-DNA complexes in vivo. Methods Enzymol. 1991;208:146–168. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)08012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer M. R., Golden S. S. Light availability influences the ratio of two forms of D1 in cyanobacterial thylakoids. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7412–7417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straney D. C., Crothers D. M. Intermediates in transcription initiation from the E. coli lac UV5 promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):449–459. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tandeau de Marsac N. Occurrence and nature of chromatic adaptation in cyanobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):82–91. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.82-91.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Marsac N. T., Cohen-bazire G. Molecular composition of cyanobacterial phycobilisomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1635–1639. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]